Norwich was slow to find its way into the industrial world. Before the slum clearances, the city still had a timber frame: largely Tudor in appearance with Georgian contributions. Around 1900 the architect Edward Boardman introduced a glimpse of modernity with factories and offices built around steel frames with concrete floors, while George Skipper’s more exuberant projects added sparkle. The contributions of these two Norwich titans survived well, helping to define the city’s present-day character, but much of the fine texture from a century ago was built up by numerous smaller practitioners like Cecil Upcher.
Upcher was born in 1884 in Barnham Broom, Norfolk, where his father, the Reverend Arthur Charles Wodehouse Upcher B.A., was the rector.

White’s Directory described Reverend Upcher’s home as ‘a spacious residence with pleasant grounds near the church’ [2]. The 1911 census records that the Upchers lived in the rectory with a cook, a parlour maid, a house maid, a kitchen maid and a nurse. They lived well, in a manner appropriate to the descendants of Abbot Upcher, the man who commissioned the Reptons to design Sheringham Hall and Park.

Having mentioned Abbot (his given name, not title) Upcher it would be wrong to cast him aside so soon for in some quarters he is the better known Upcher. The name Upcher may be a corruption of Upshire in Essex yet census returns find it most frequently – although still scantly – in Norfolk [3]. In 1812, Abbot and Charlotte Upcher bought their estate near Upper Sheringham on the north-east Norfolk coast. They engaged John Adey Repton as architect and Repton’s father Humphry to reconfigure the landscape.
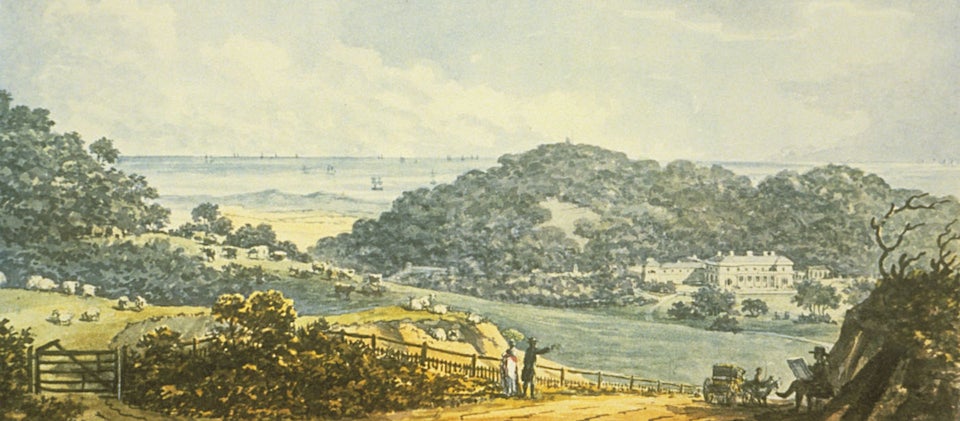

Humphry Repton (b1752), the foremost landscape designer of the late Georgian period, died in March 1818, seven years after being badly injured in a carriage accident. In less than a year Abbot Upcher, would also die, aged 35, never to live in the hall he had commissioned.
Abbot’s great grandson Cecil therefore came from Norfolk stock and it was as a Second Lieutenant in the 9th Battalion of the Norfolk Regiment that he served in the Great War.

Writing to his fiancée, Hilda Ward, he describes the conscripts as “a top hole lot of men all true Norfolk men” [4]. In his letters Upcher describes several of his billets; some he sketched.

Since 1906, Upcher had been in practice in Norwich as an architect, specialising in church restoration. His professional training emerges in the sketch below in which he measured the accommodation provided by a dugout: beneath a ceiling four feet high were two beds, six feet long and two feet wide, separated by an 18 inch gap. His temporary refuges were drawn with precision but revealed nothing about the awfulness on the other side of the tin roof.

Upcher’s letters convey the sense of the ironic, understated tone of the officer class – especially when wounded.
‘Monday September 27th 10am [1915]. In the train. Here I am on my way to England I believe. I got a bullet through the fleshy part of my left thigh. No damage and as fit as a fiddle. Feeling a bit of a humbug to be leaving it all, but walking is rather a job at present. We had to take a Bosch position at 7am yesterday Sunday morning and I got bowled over with a lot of others I fear [4].’
The voice will be familiar to readers of PG Wodehouse (and the name, Wodehouse, introduced into the family line by Upcher’s grandmother is inescapable here). When asked if he had taken part in the First World War, Bertie Wooster’s manservant Jeeves replied, ‘I dabbled in it to a certain extent, m’lord.’ (Ring for Jeeves, 1953).
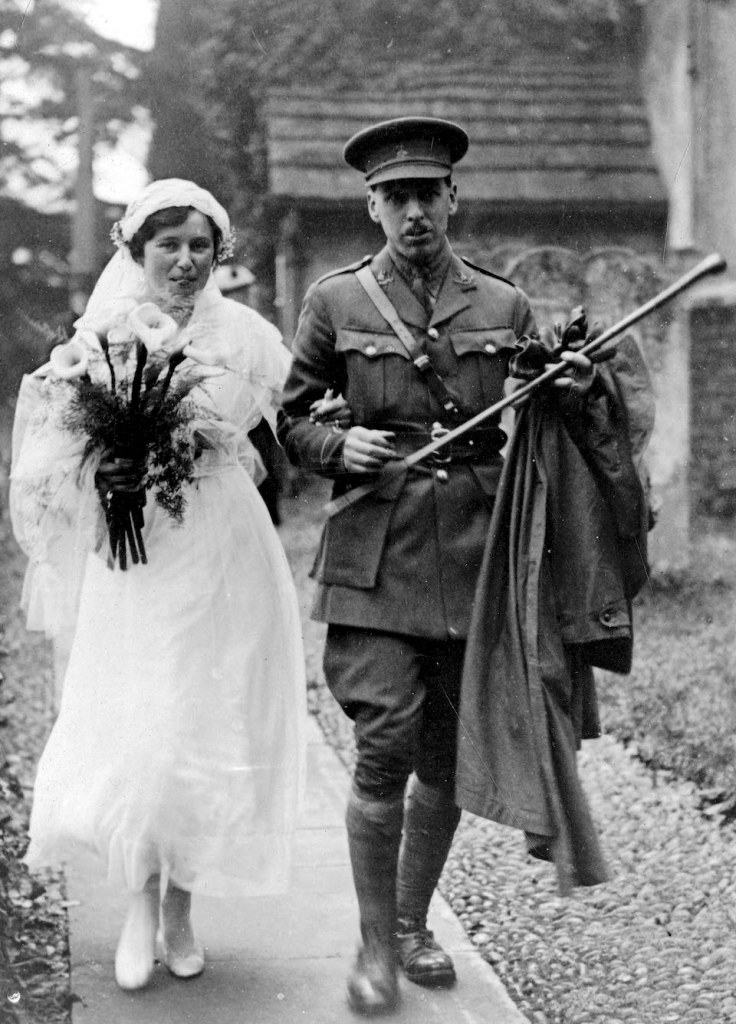
By mid-1916 Upcher was suffering from deep depression and was invalided out with shell shock [5]. When he married Hilda the same year we see him holding a cane that seems too large for a swagger stick, suggesting he was still carrying an injury. Nevertheless, he returned to active service until the end of the war.

Upcher had been educated at Haileybury College, Herts before training at the Liverpool School of Architecture. Before the war, he was in partnership with Arthur John Lacey at number 6 Upper King Street Norwich. They specialised in church renovation and one of their last projects before the outbreak of war was the restoration of the ruinous St Martin, Overstrand.
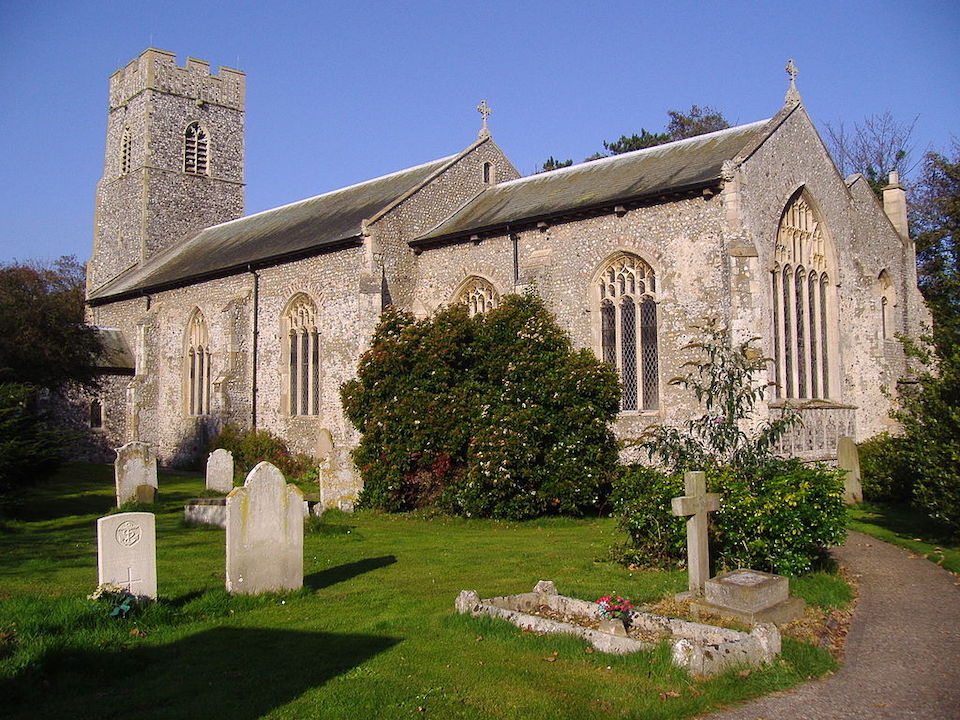

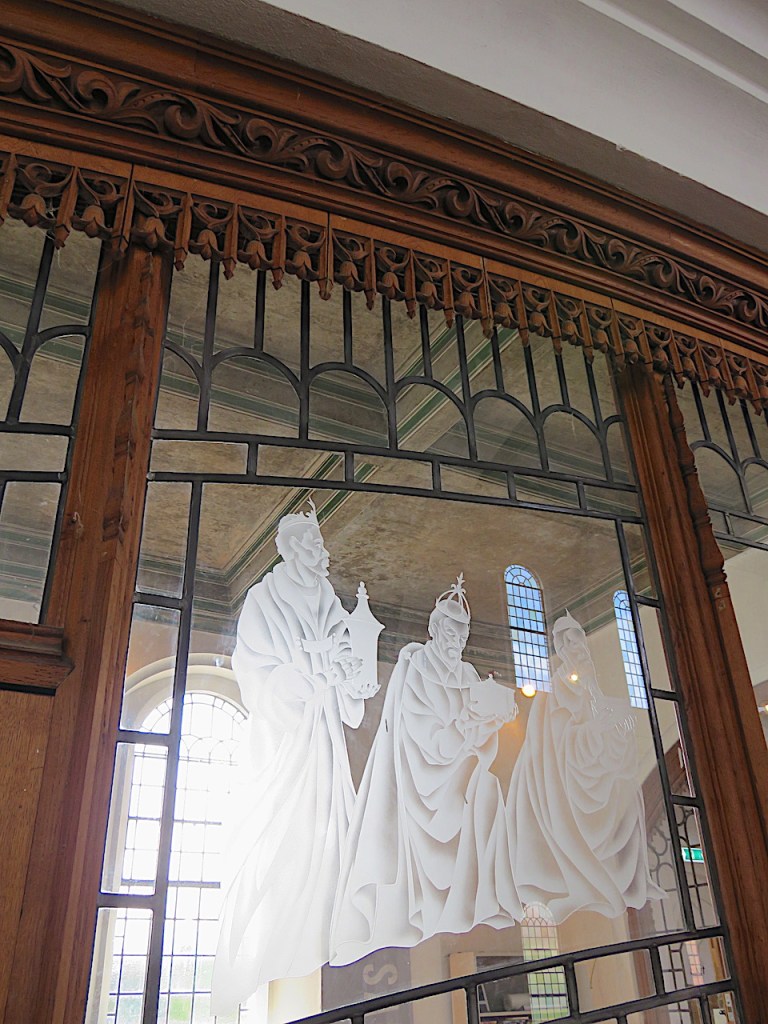
After the war, in the church in Upper Sheringham that housed the Upcher mausoleum, Cecil Upcher acknowledged men of the village killed in the war, by designing the oak pulpit and the foliate reredos above the altar.
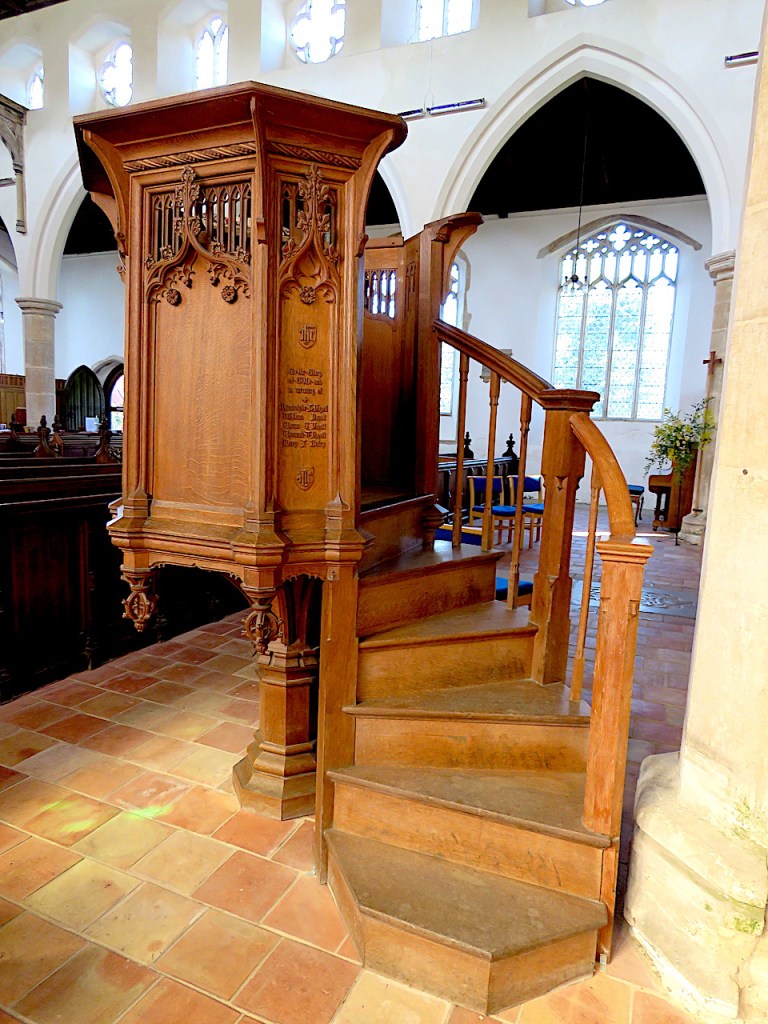

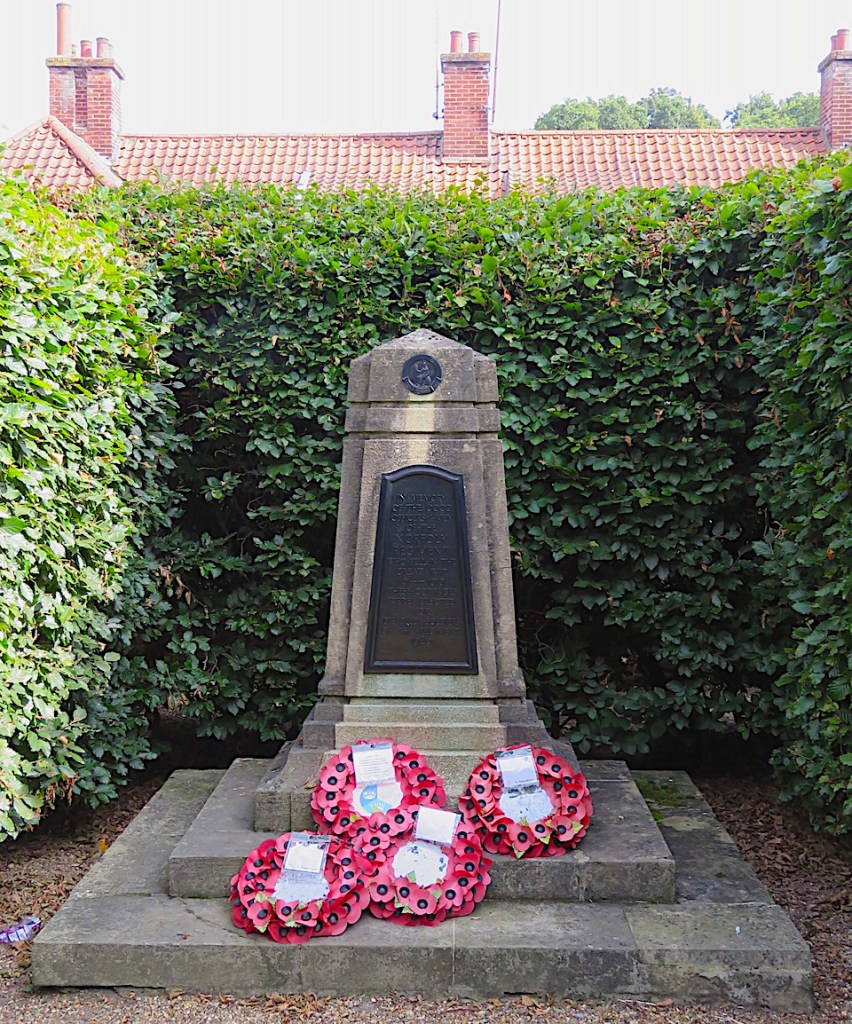
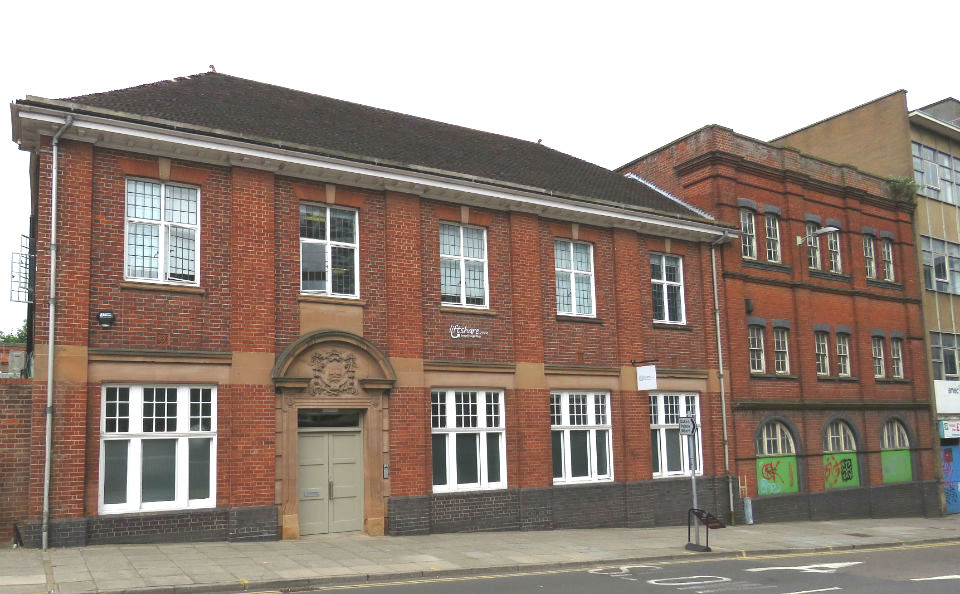
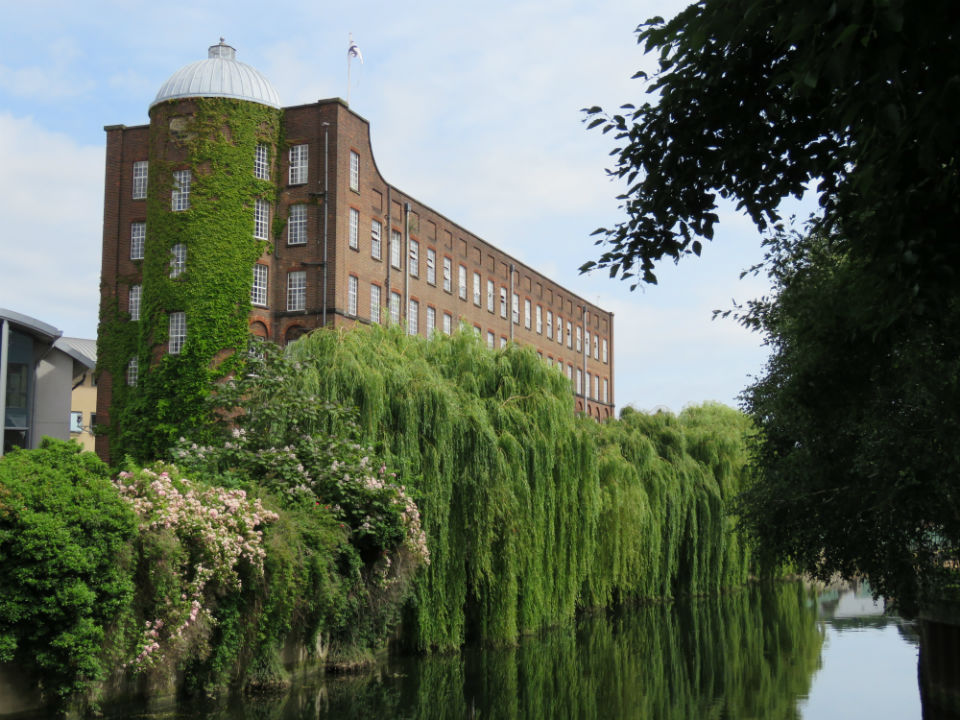
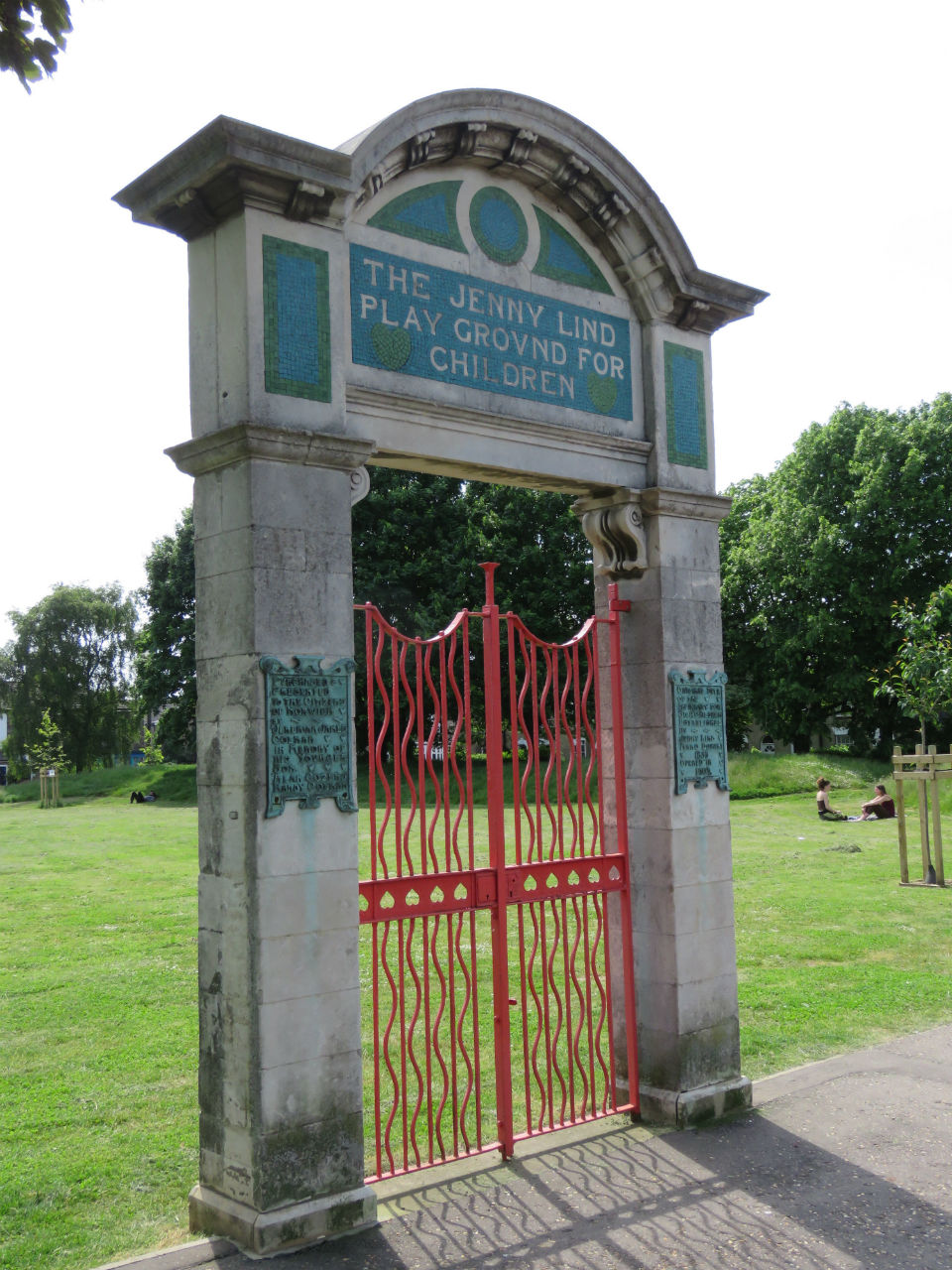
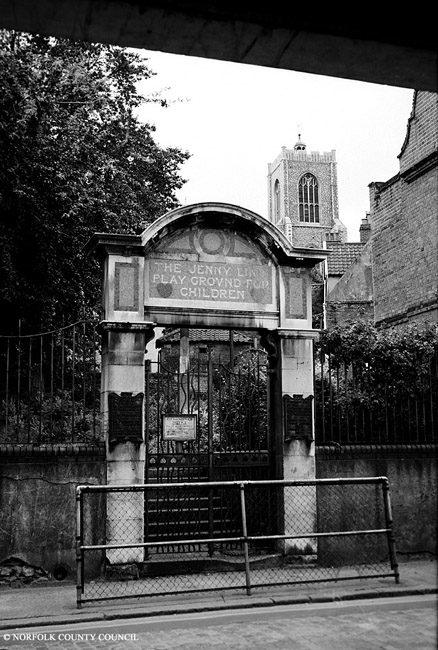
And as a memorial to the men of the Norfolk Regiment who died in the Great War, Upcher designed a crescent of 12 alms houses in Norwich for disabled soldiers.


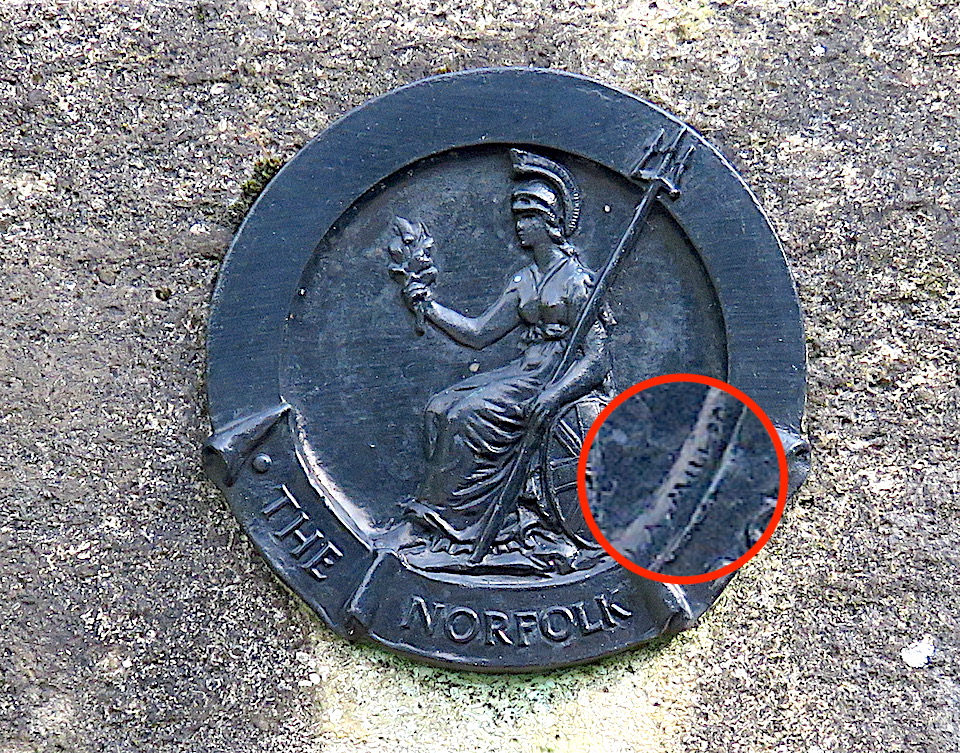
The medallion of Britannia at the top of this memorial is signed by HA Miller who collaborated with Upcher on a memorial in the cathedral [6]. Herbert Miller (1880-1952), who trained at the Norwich School of Art, seems to have specialised in memorial plaques with portrait roundels, including: Amelia Opie on Opie House in Castle Meadow; John Sell Cotman on Cotman House in St Martin-at-Palace Plain; George Borrow outside George Borrow House in Willow Lane; and the Baptist preacher Joseph Kinghorn on a house in Pottergate near the Grapes Hill underpass [7].

After the Second World War Upcher was to design, for an adjacent plot, a range of six cottages for the wounded, funded by the public via The Home Guard. Distinguished by their Dutch gables, these cottages seem to belong to an earlier age; they appear less generous than the two-storey accommodation provided by the Great War cottages but were designed for the disabled as single-storey bungalows in order to avoid difficulties with stairs.

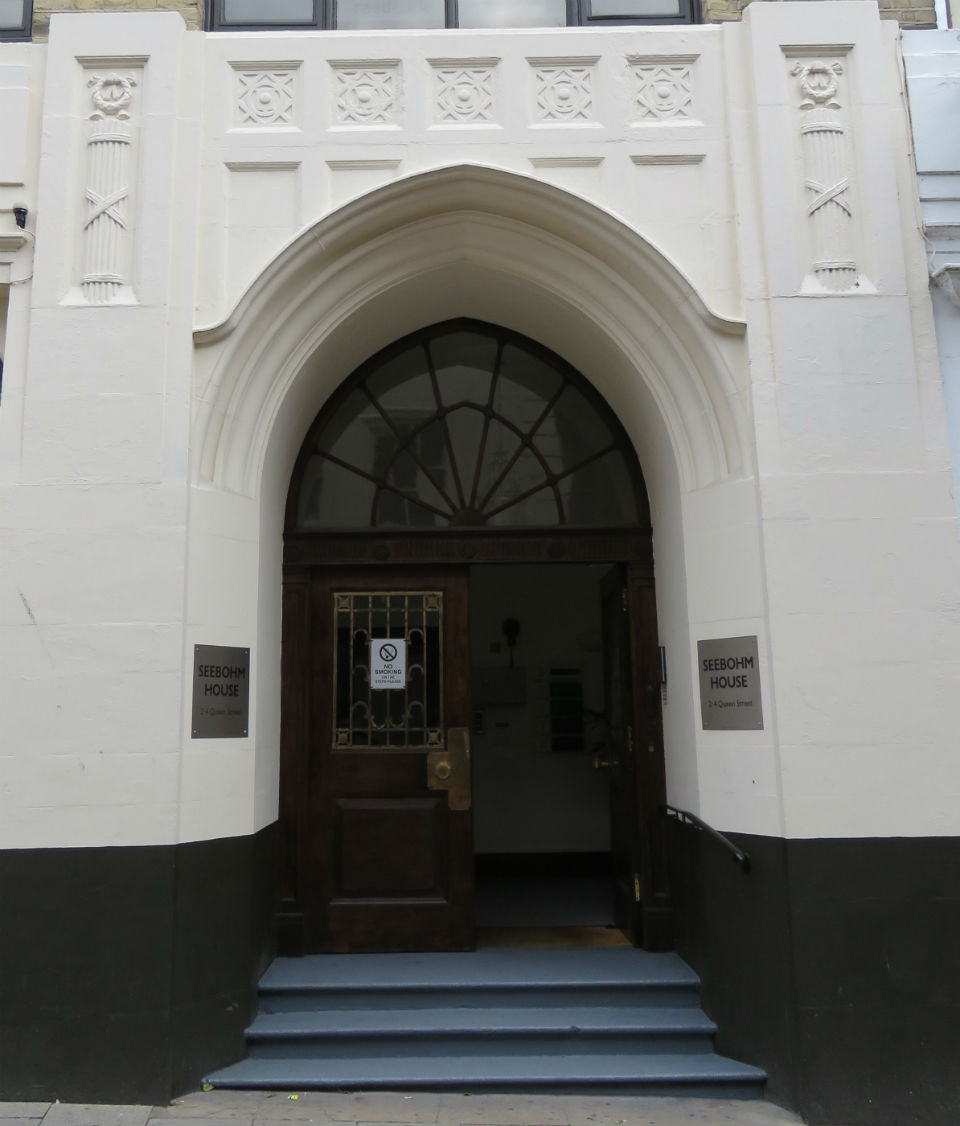
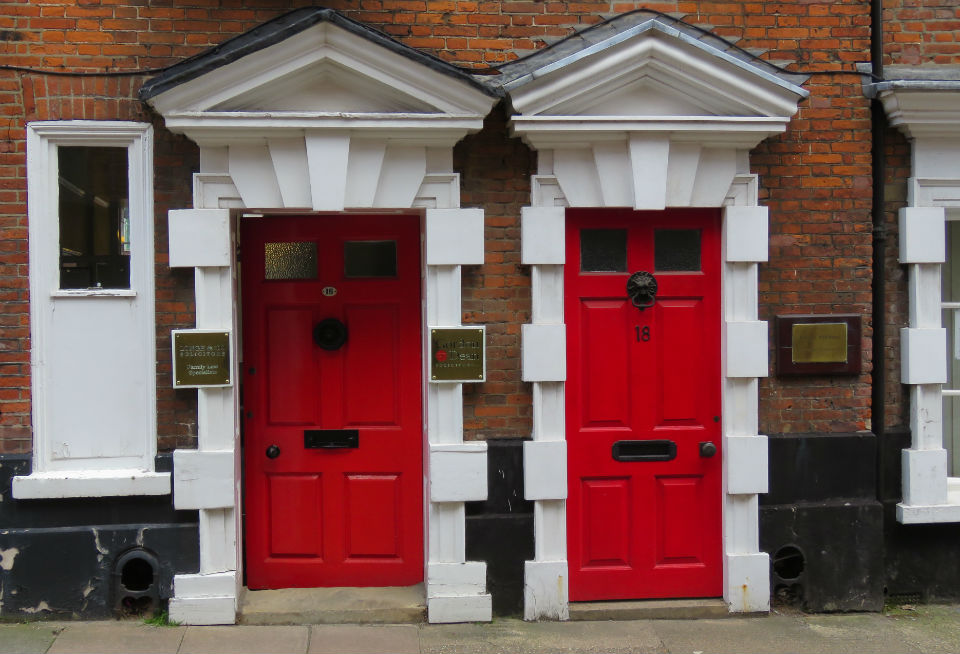
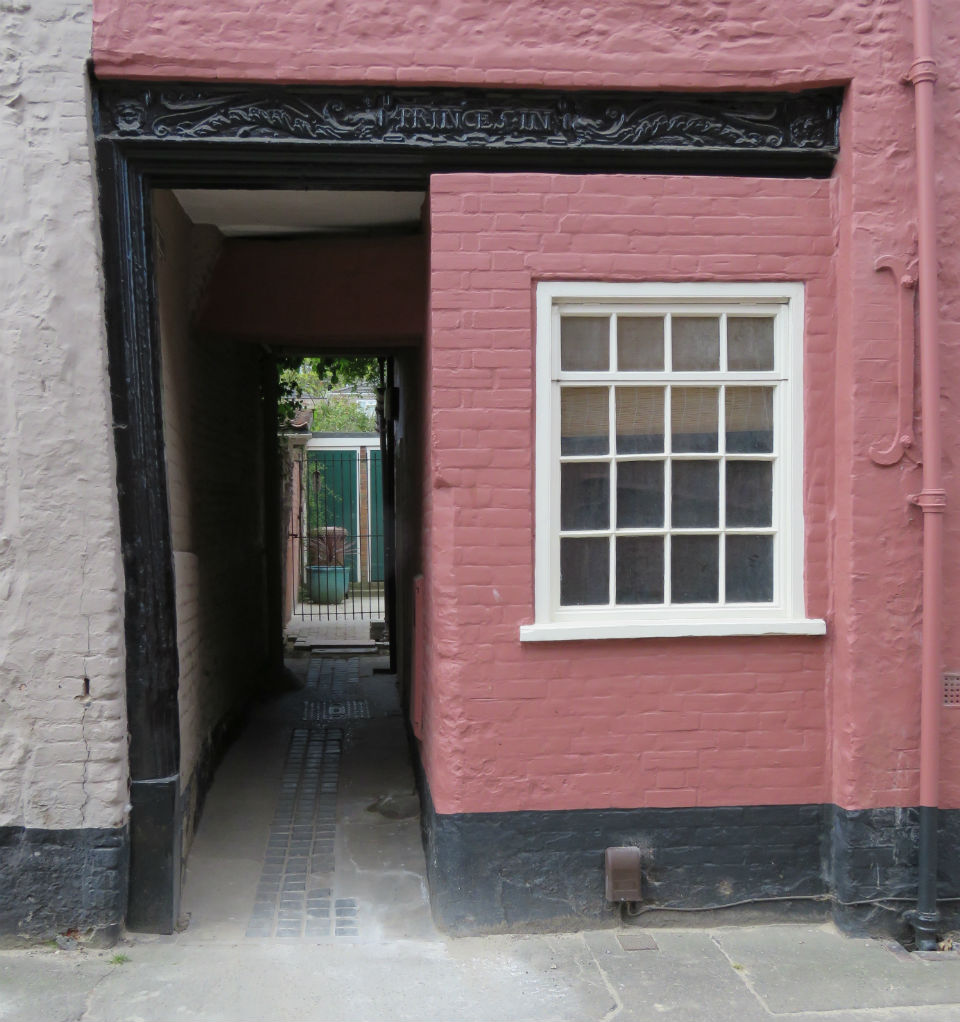
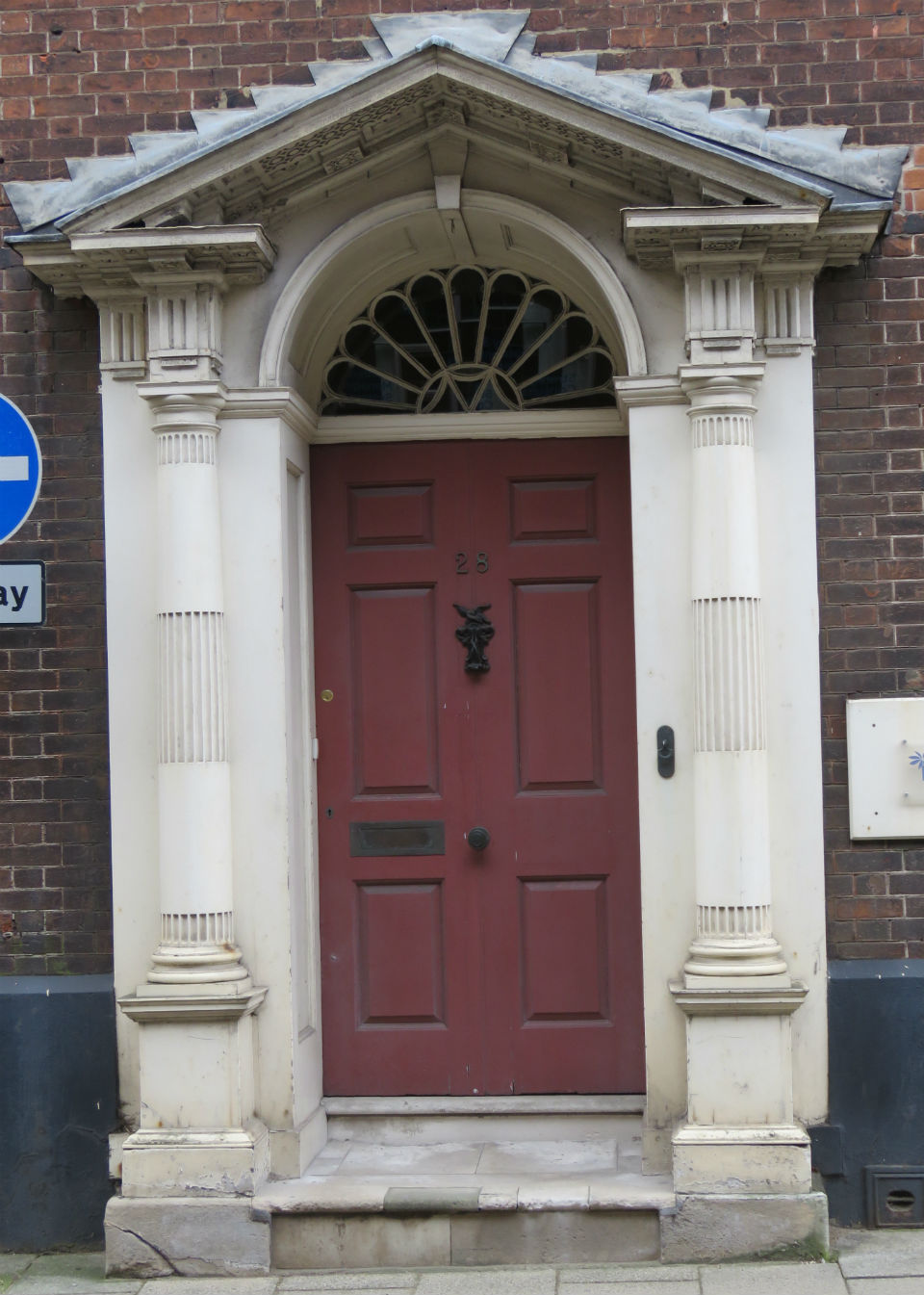
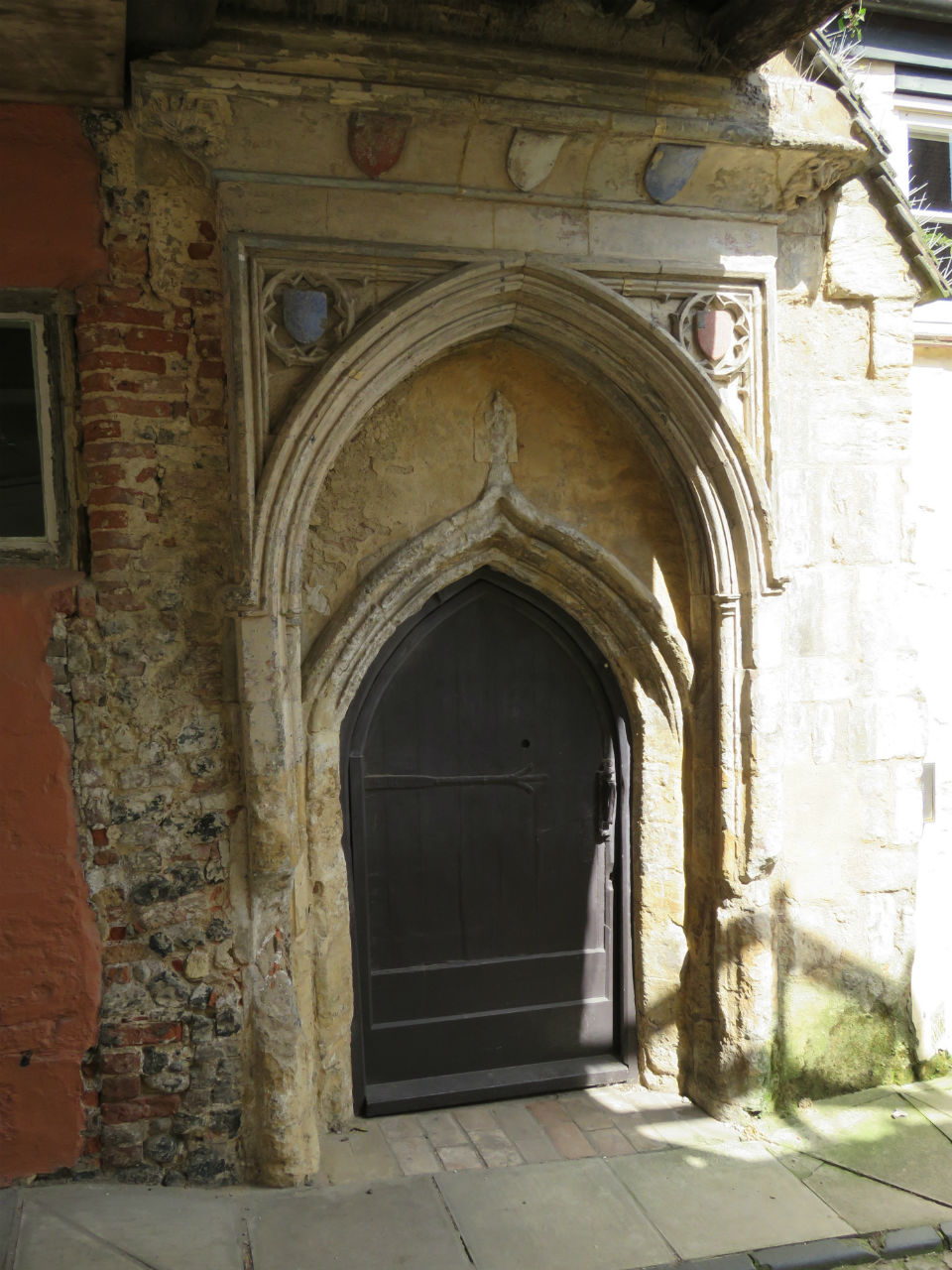
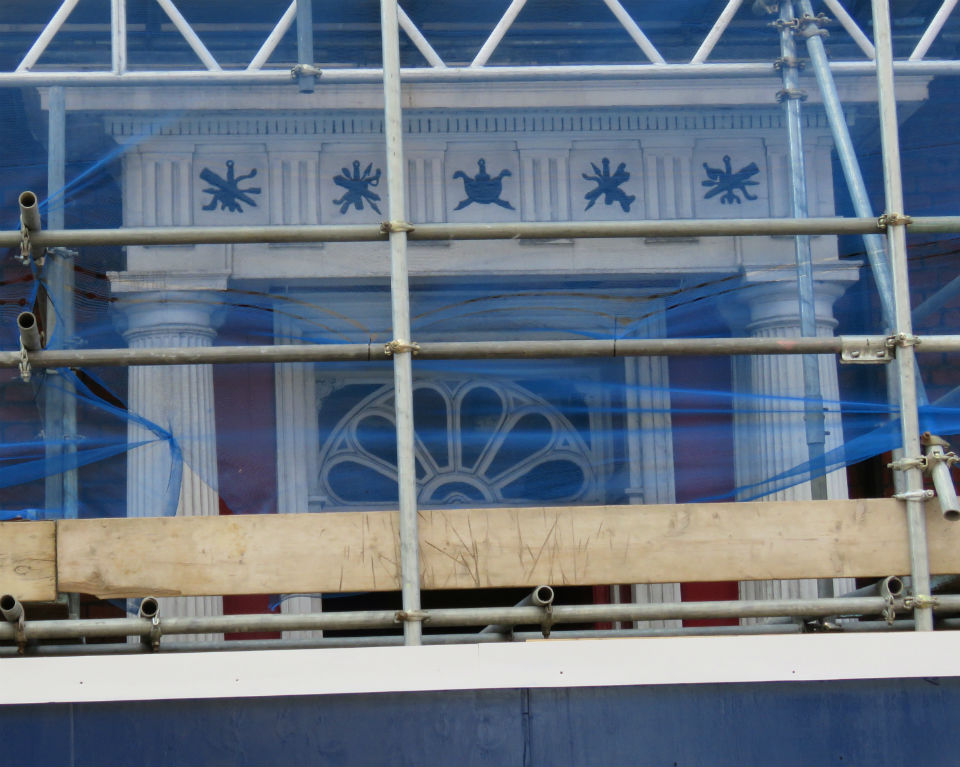
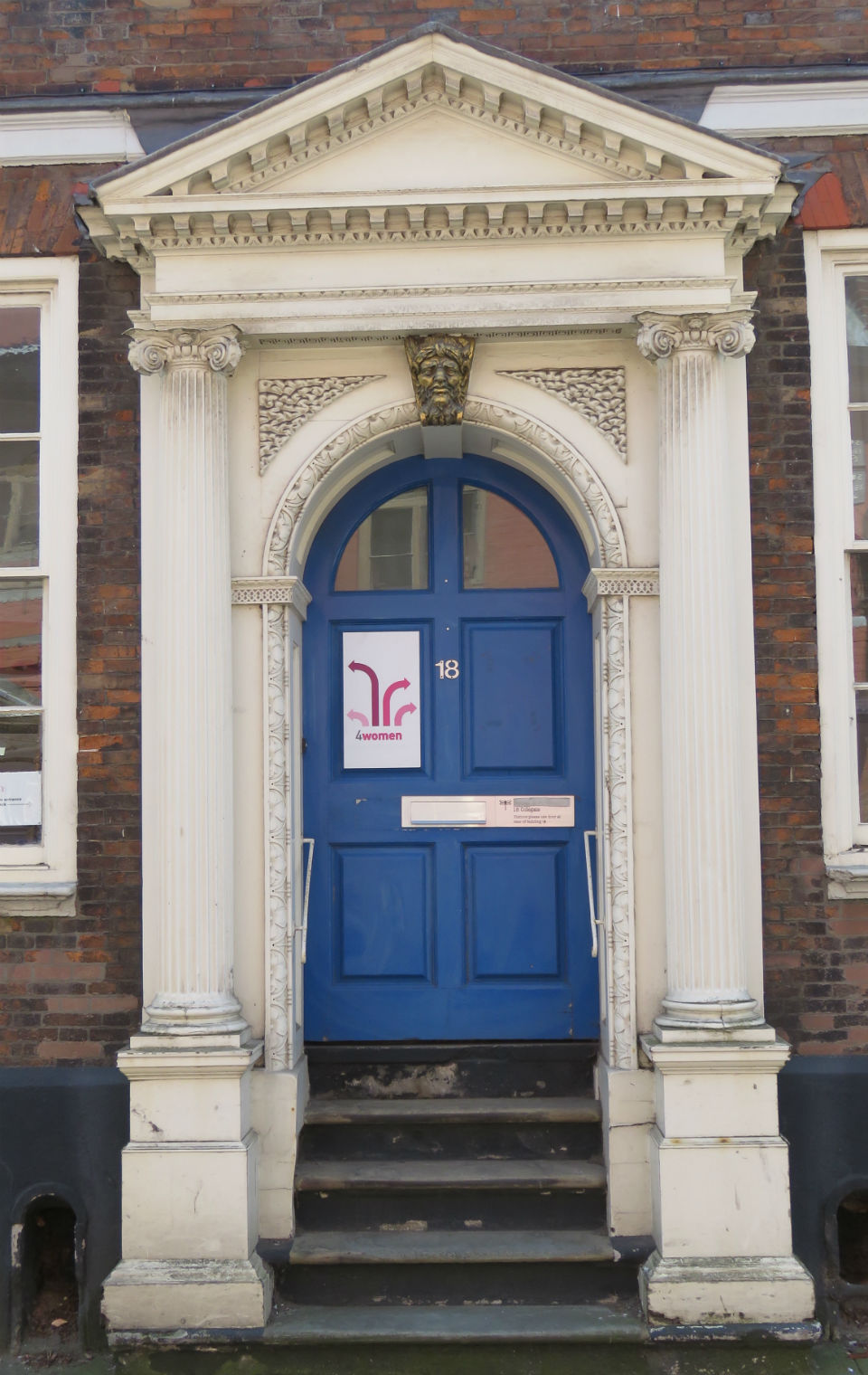
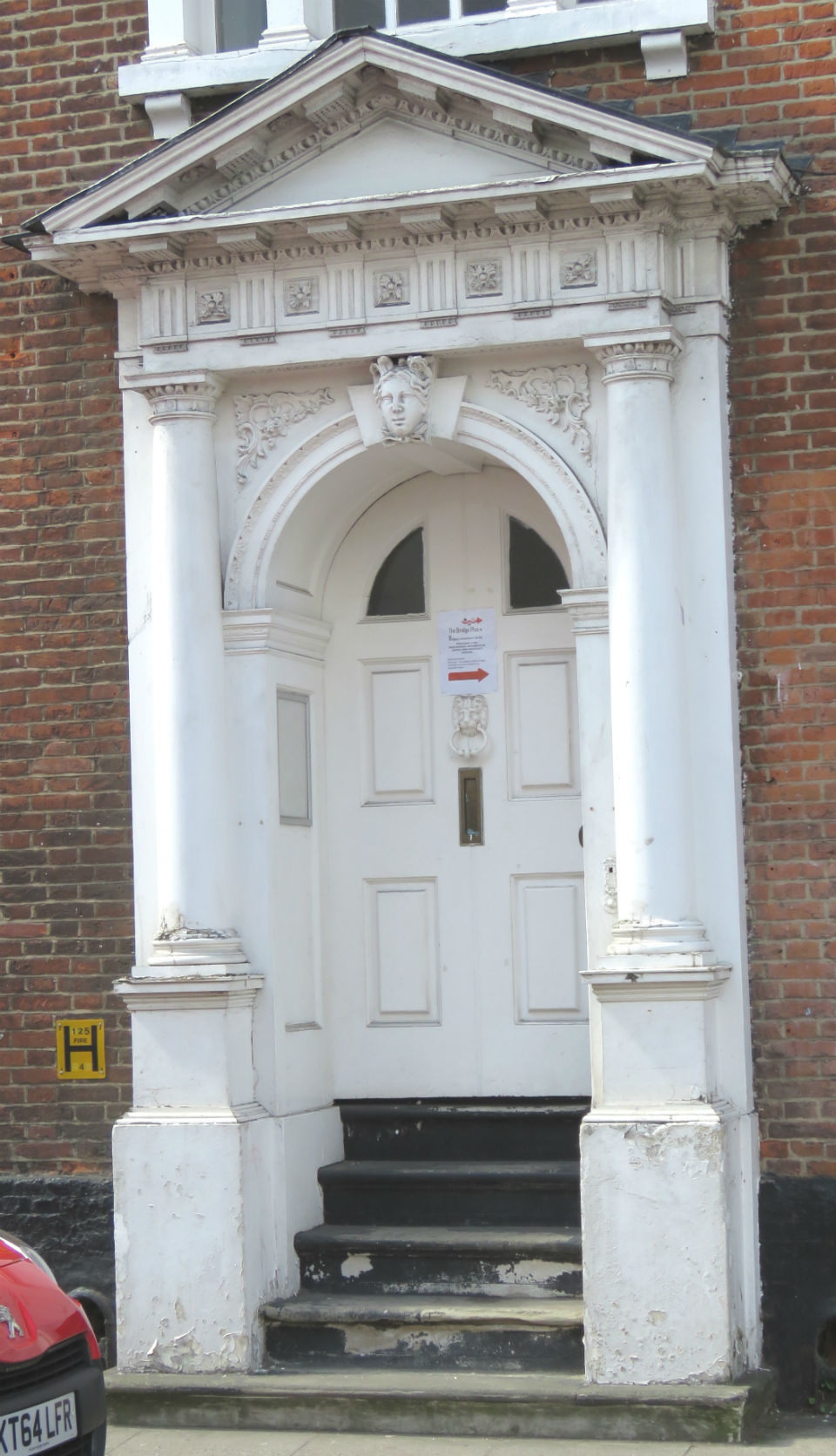
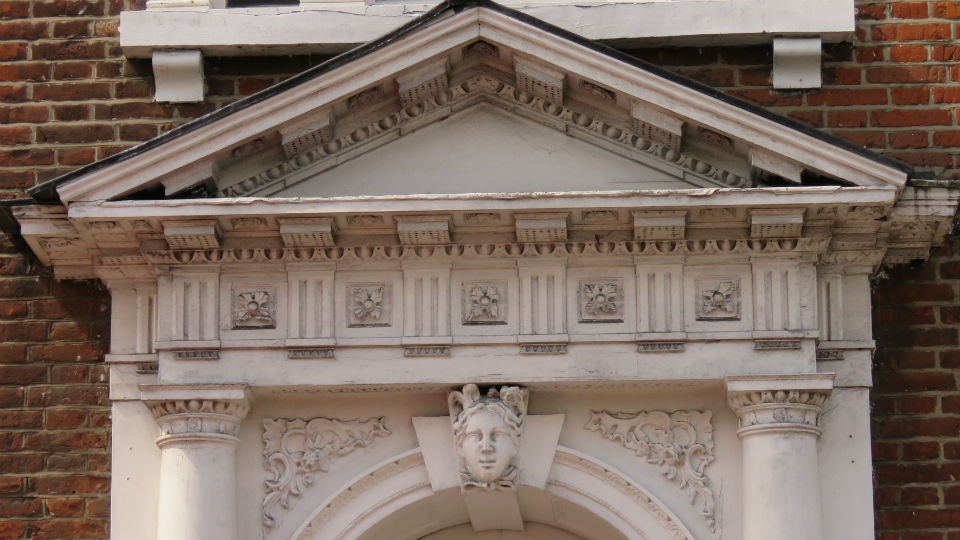
Documents in the Norfolk Record Office confirm that Upcher’s practice was involved in all aspects of restoration in churches around Norfolk. They were not, however, restricted to ecclesiastical work; for example, Number 24 Princes Street is a Tudor building restored in 1932 by Upcher. Stripping the plaster from the front revealed the herringbone brick infill we see today. According to George Plunkett, the wooden lintel above the door came from a house in Fyebridge Street, once home to Edmund Wood who was Sheriff in 1536 and Mayor in 1548 [8].
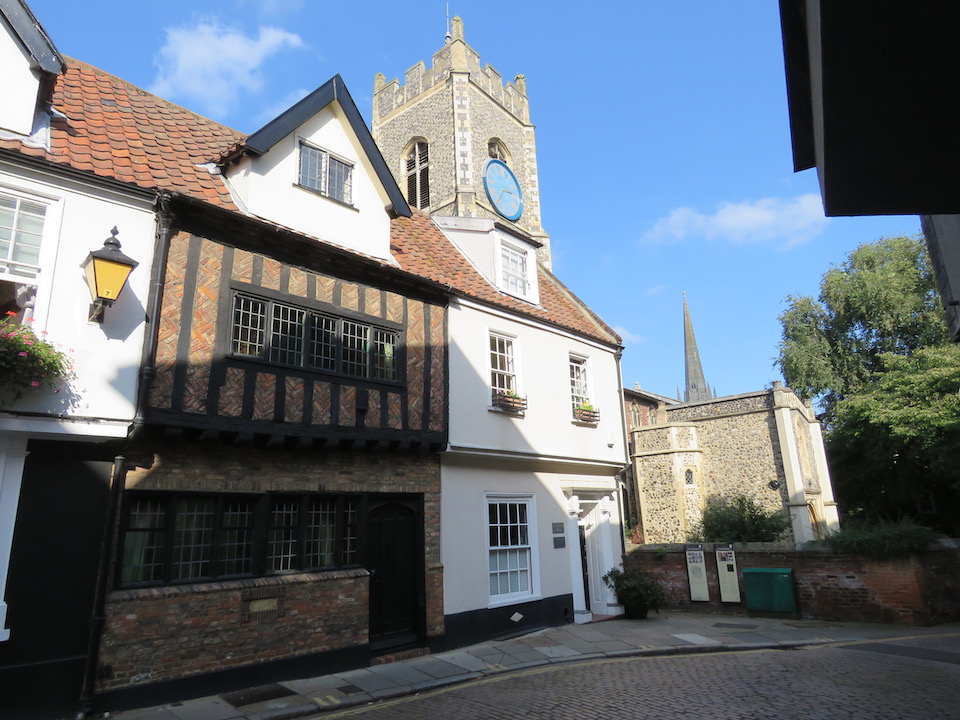

The repurposed spandrels of No 24’s door contain the merchants’ mark of the Worshipful Company of Grocers (top right, below). And around 400 years later, Cecil Upcher and builder Robert Carter left their names carved on the door jambs of the house in Princes Street.

The mark of the Mercers’ Company is also suggested to be represented somewhere [8] but the shield at top left contains a tangle of initials and not the maiden’s head that was, from 1530, the mercers’ mark, a fine example of which can be seen in nearby Elm Hill.

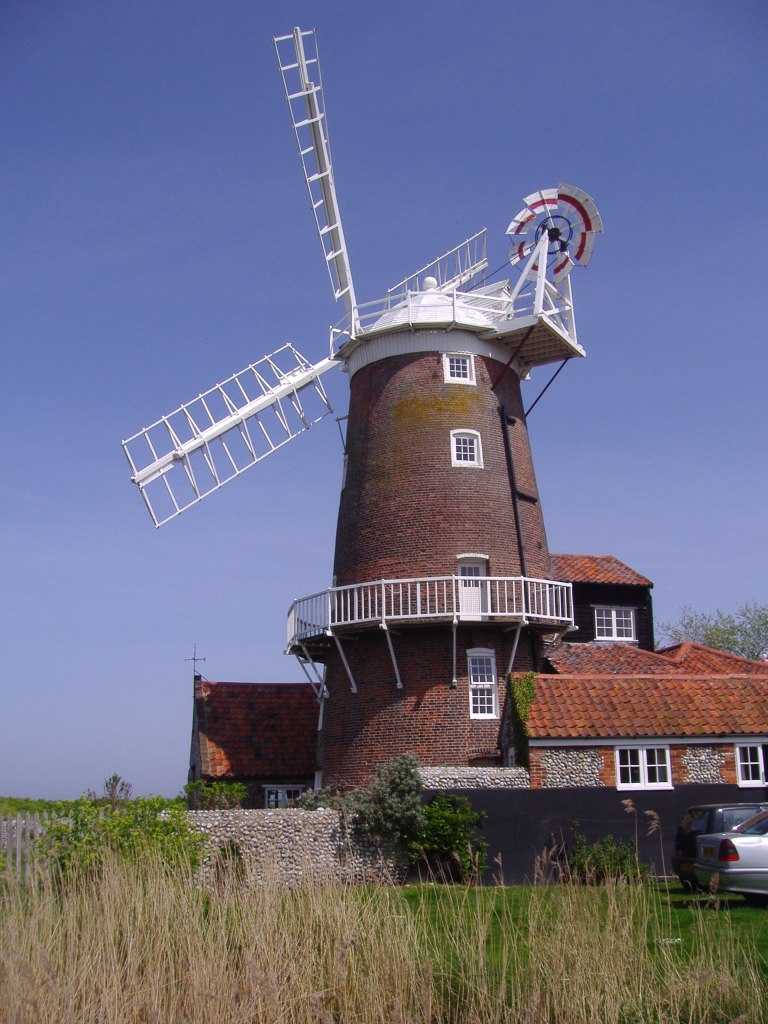
Cley Windmill in North Norfolk also received Upcher’s attention.

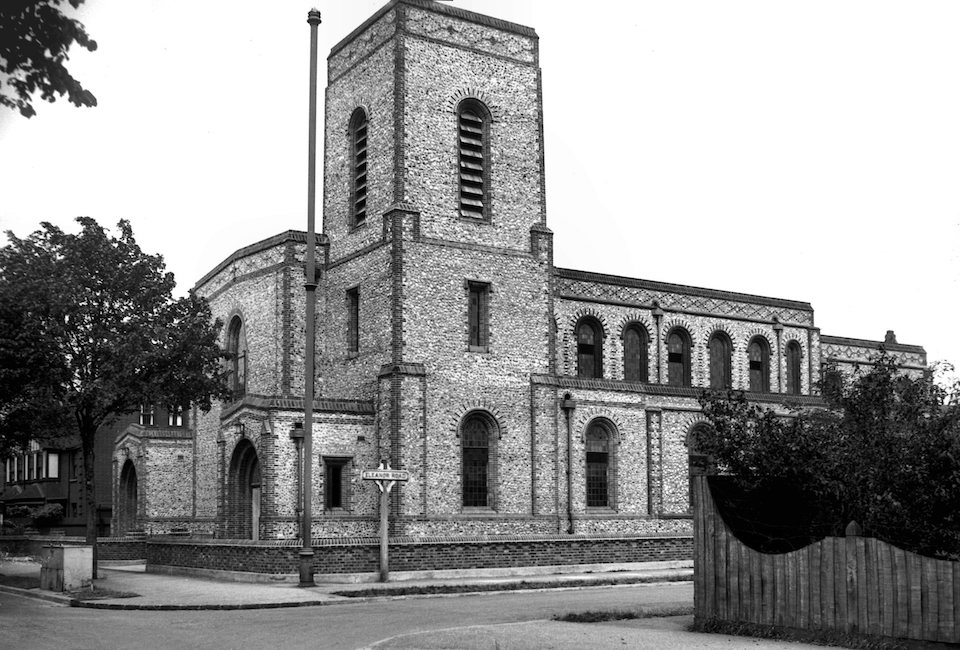
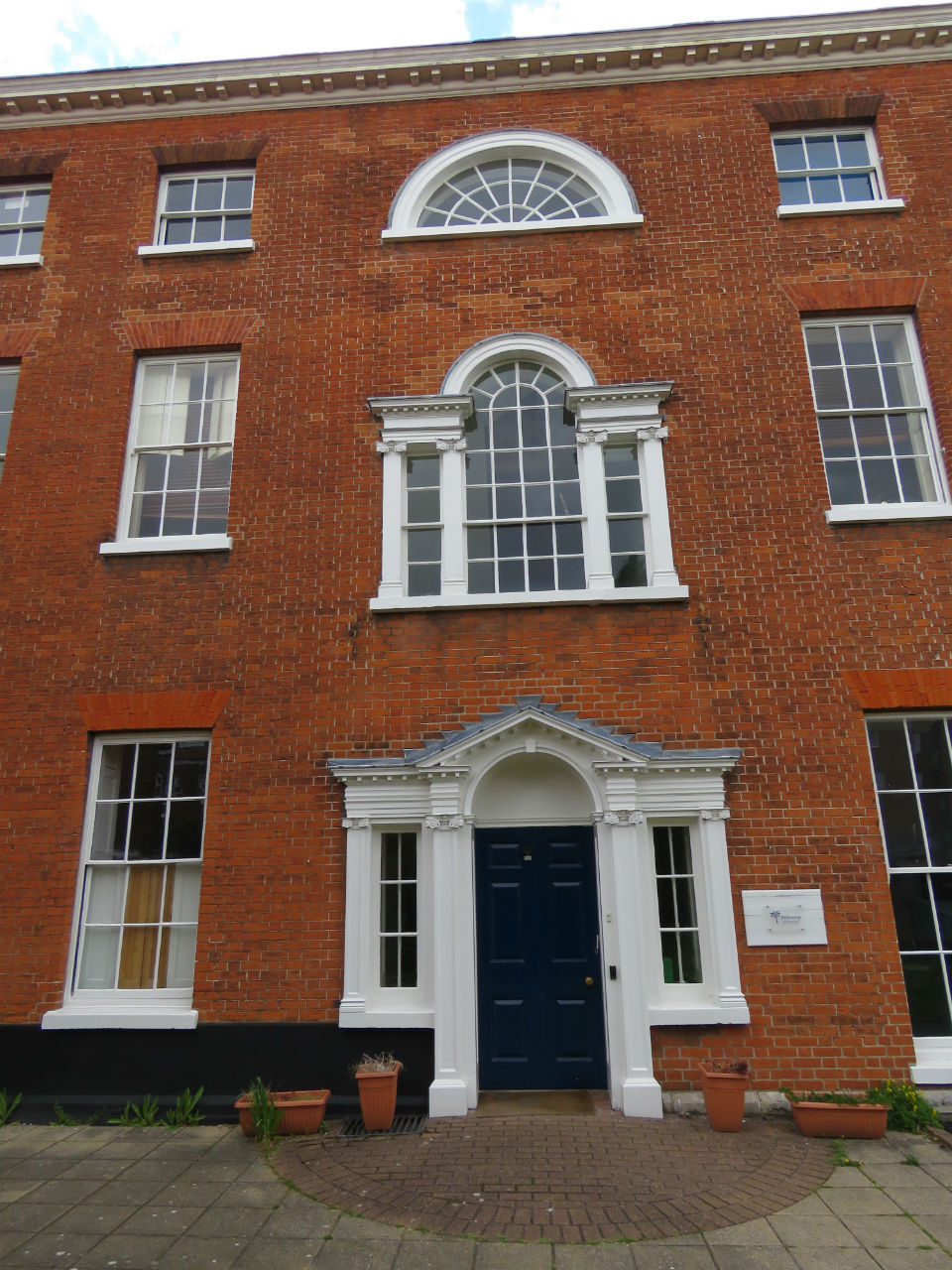
In the last years of the nineteenth century, when the city was expanding beyond the city walls, the Trafford estate in the parish of Lakenham was developed on land owned by Edward Southwell Trafford. In 1919 his son, WJ Trafford, extended the estate around Eleanor and Trafford Roads and in the early 1930s Upcher designed a church for the new community. As one of the few churches built in Norwich between the wars St Albans was very much in keeping with the surrounding detached villas – comfortable yet somehow ’modern’.

Pevsner and Wilson [9] called the style, ‘vaguely E.E.’, although the church’s rounded arches are clearly at odds with the lancets of Early English. By adopting a ’free’ Norman style, before the incursions of the architectural Goths, Upcher may have been differentiating his new church from the work of the Gothic revivalists of the previous generation. See, for example, the recent post on the campaign of Nonconformist church-building by Norwich architect AF Scott before the Great War [10]. Scott, incidentally, was still alive when St Albans was being built.
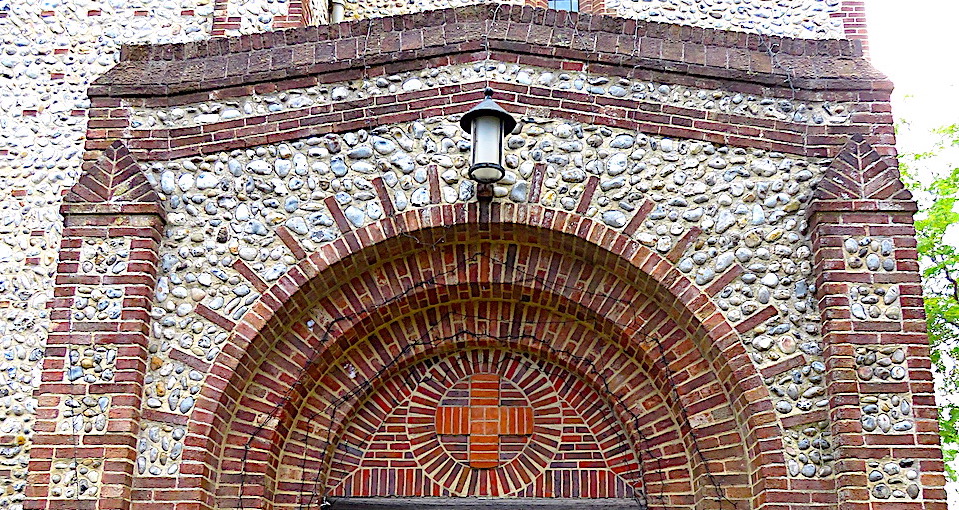

What the building is is vernacular. No imported stone here, its craftsmanship expressed in local materials drawn from Norfolk soil: unknapped flints with red-brick dressings. Pevsner and Wilson [8] described St Albans as being, ‘In the Maufe succession,’ suggesting a link with Sir Edward Brantwood Maufe (né Muff) whose first major commission was Kelling Hall in north Norfolk.
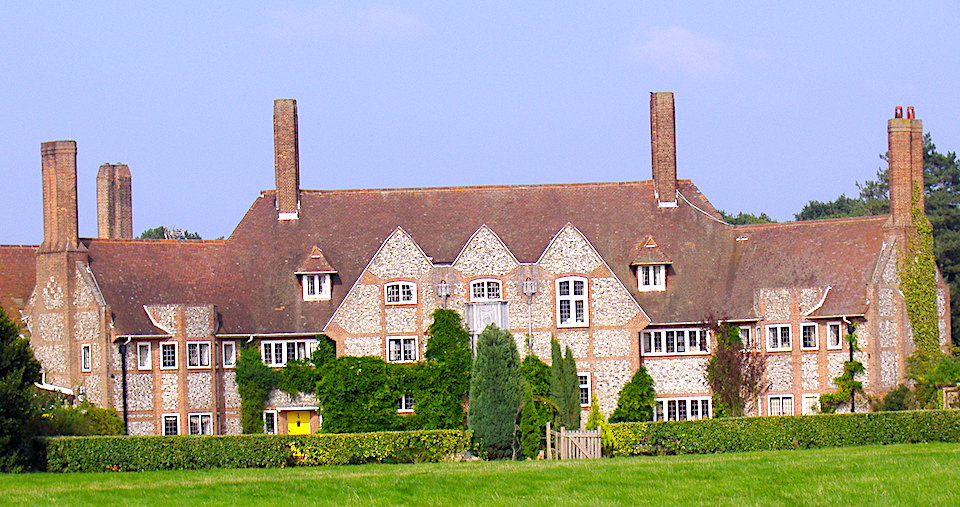

Following Norfolk’s two other butterfly houses – Happisburgh Manor in 1900 (by Detmar Blow) and Voewood in 1903 (by ES Prior) – Kelling Hall was built in 1913 for the co-owner of the Shell Oil Company, Sir Henry Deterding. Like St Albans, Kelling Hall is clad in local flint pebbles and, in making the connection with St Albans, Pevsner and Wilson are placing Upcher’s church in the Arts & Crafts tradition.
Inside St Albans, the reinforced concrete ceiling in the chancel is a thing of beauty, predating the raw concrete of Brutalism by some 20 years – perhaps less a display of modernist leanings than an expression of the ‘truth to materials’ propagated by Pugin and Morris.
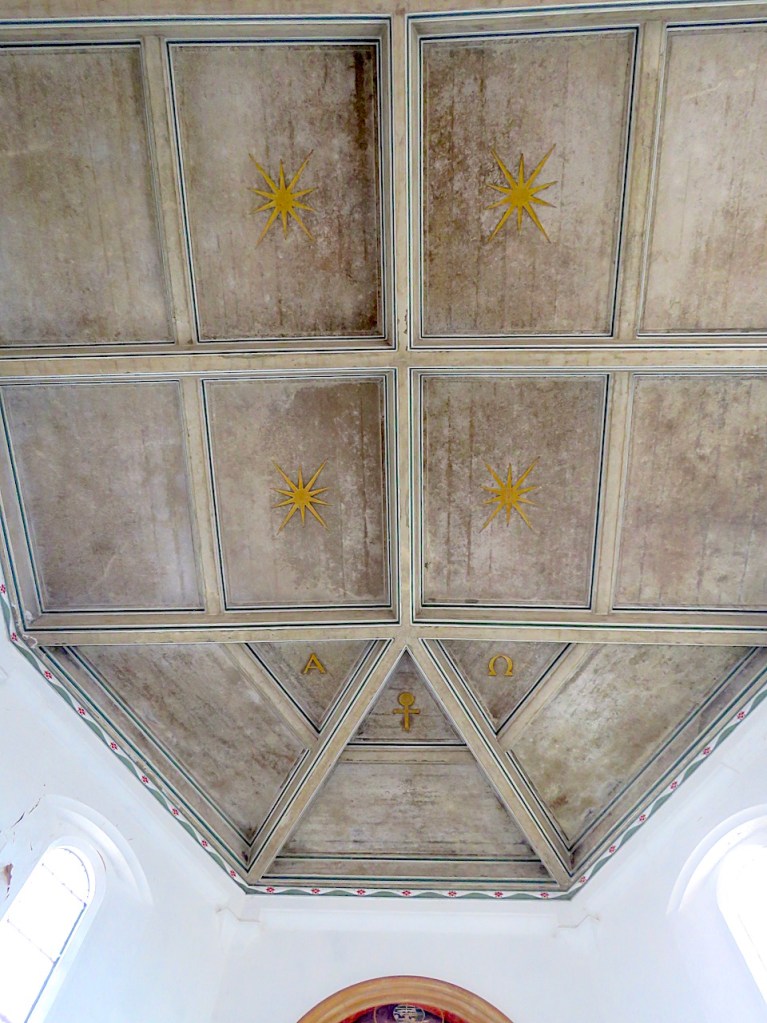

The woodwork in the chancel is reminiscent of the carving at Upper Sheringham.

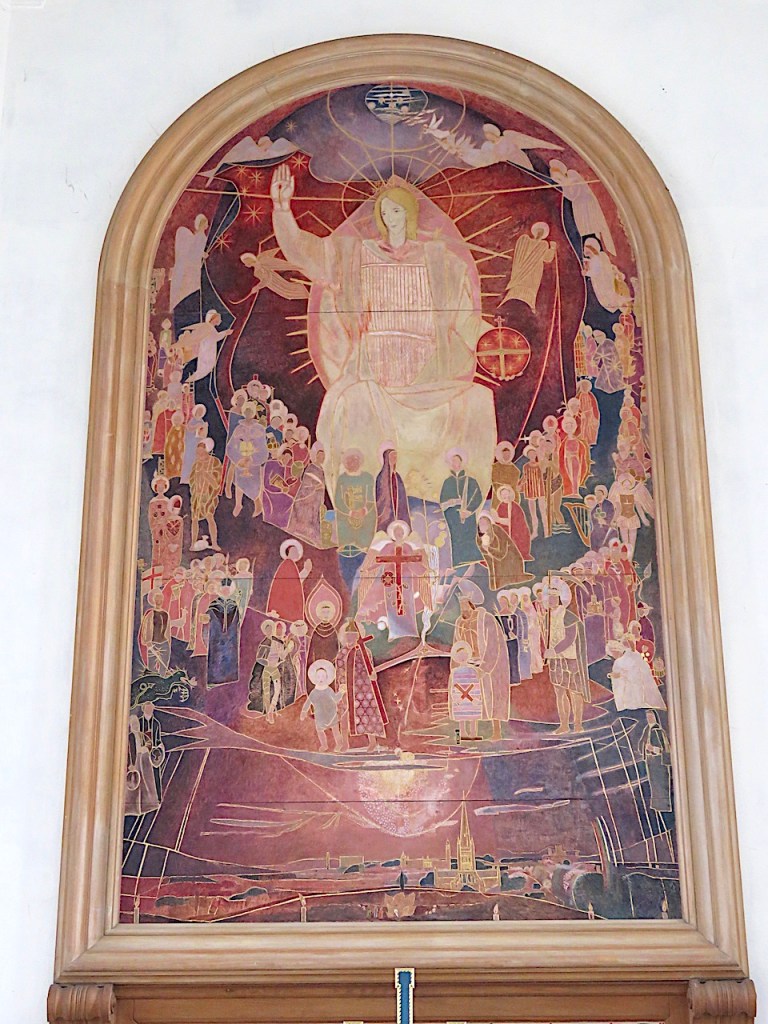
At the east end of the chancel is a large painting of an epicene Christ in Majesty, floating over the view of Norwich from Mousehold Heath. It was painted in 1955 by Jeffery Camp RA in response to a competition by the Eastern Daily Press to provide a work of art above the altar.

Upcher also designed the vicarage next door.

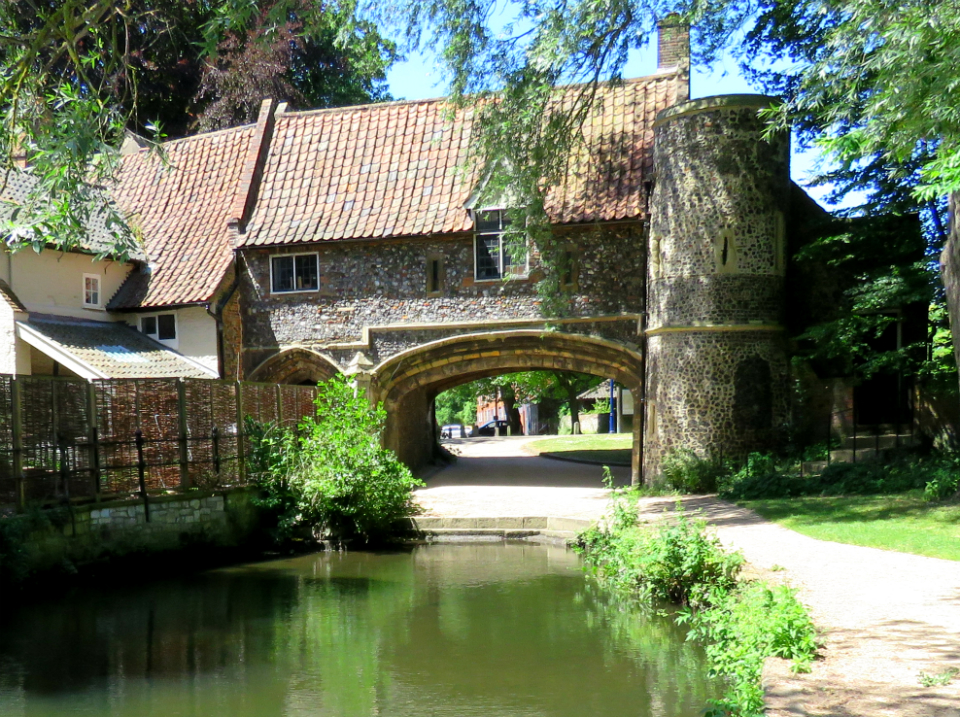
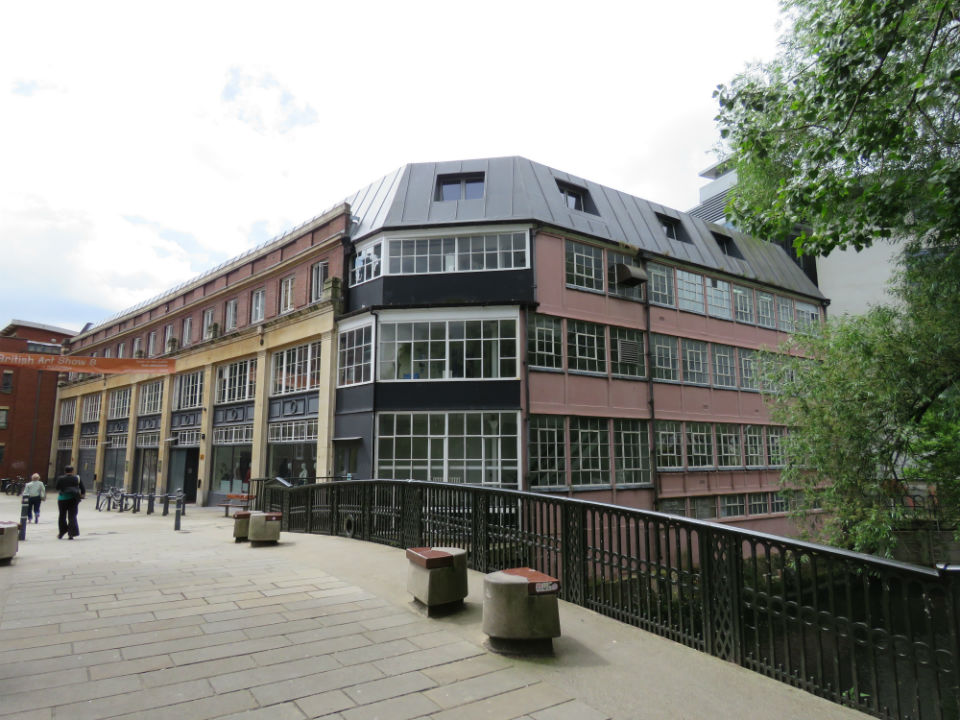
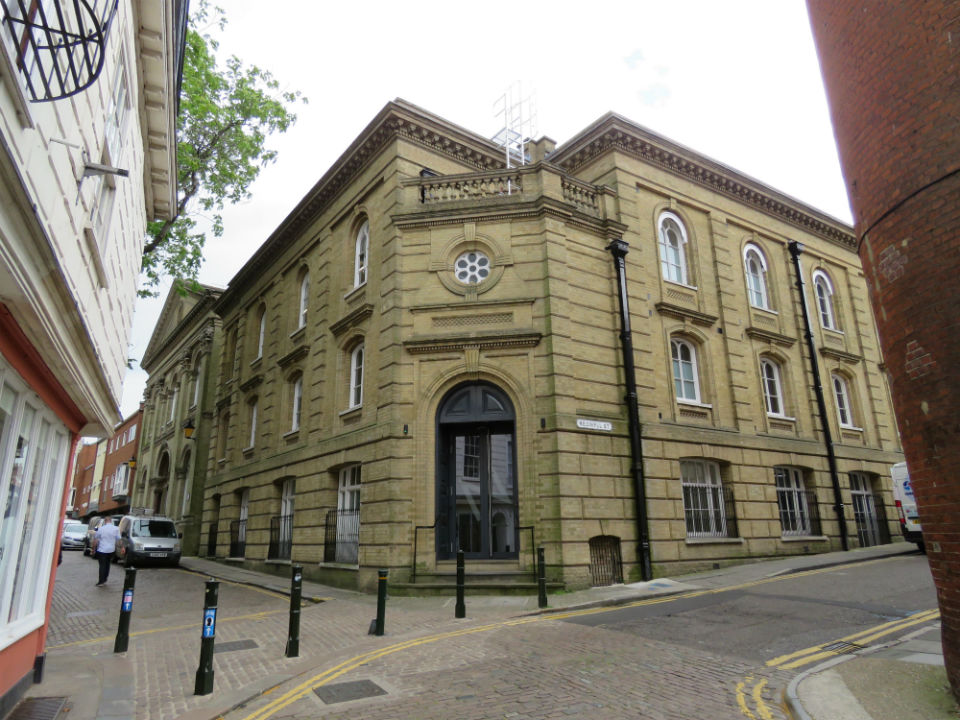
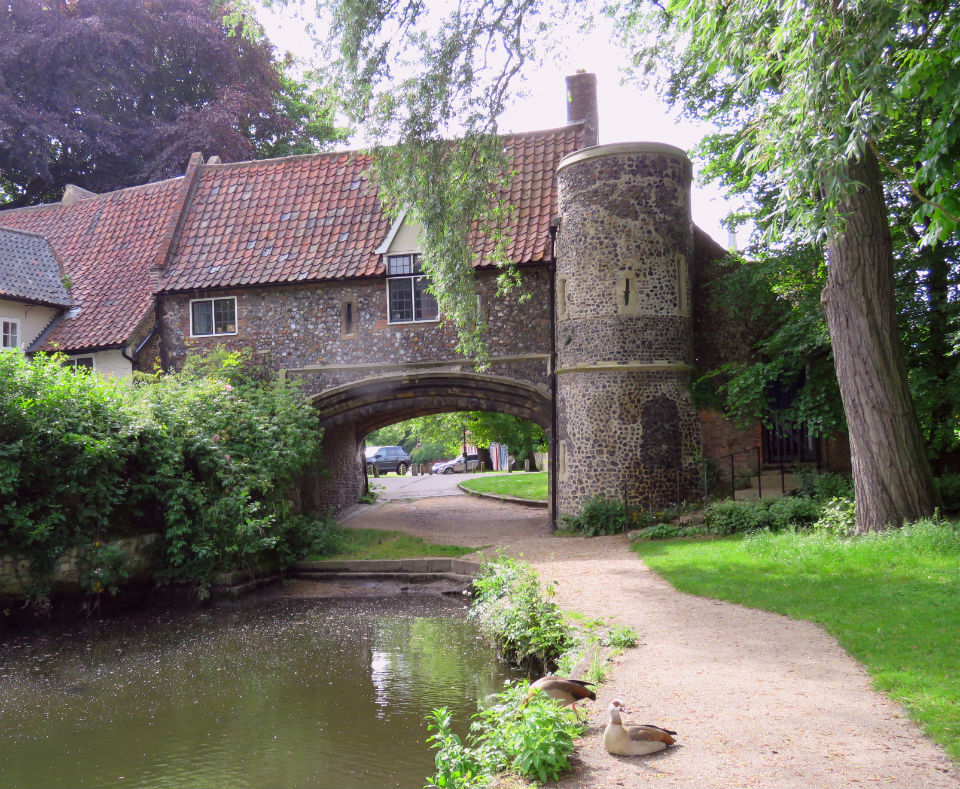
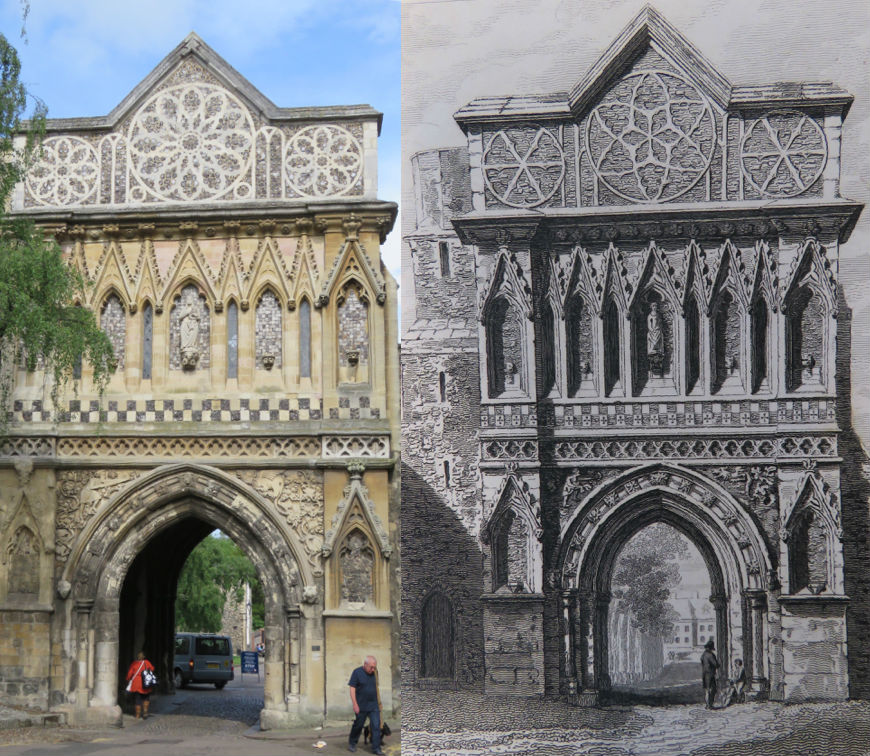
Cecil Upcher is perhaps best known for his restoration of one of the city’s most photographed landmarks: Pulls Ferry on the eastern boundary of Cathedral Close. Norwich Cathedral is faced with Caen limestone, each piece of which was shipped across the Channel. The stone was transferred to low barges behind what was to become Old Barge Yard on King Street, allowing cargo to be delivered up the narrow canal connecting the Wensum with the stonemasons’ yard inside the cathedral precinct. In the fifteenth century a flat-arched Water Gate was built over the canal and the waterway itself was filled in ca.1780 [11].

The crossing from the opposite bank of the Wensum was known for most of its life as Sandling’s Ferry [11]. This watercolour by Robert Ladbrooke, co-founder of the Norwich Society of Artists, shows us what the ferry looked like at the very beginning of the nineteenth century.
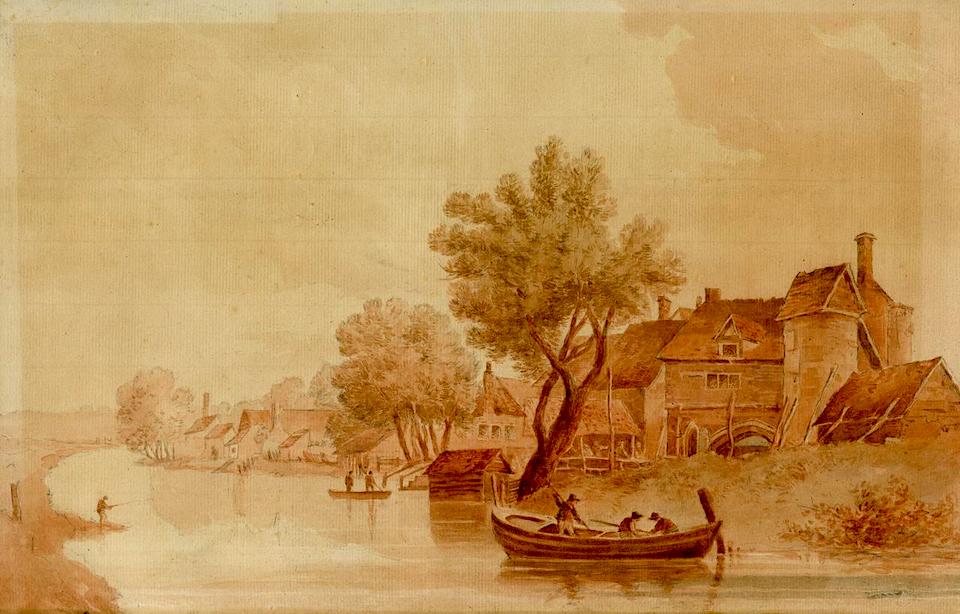
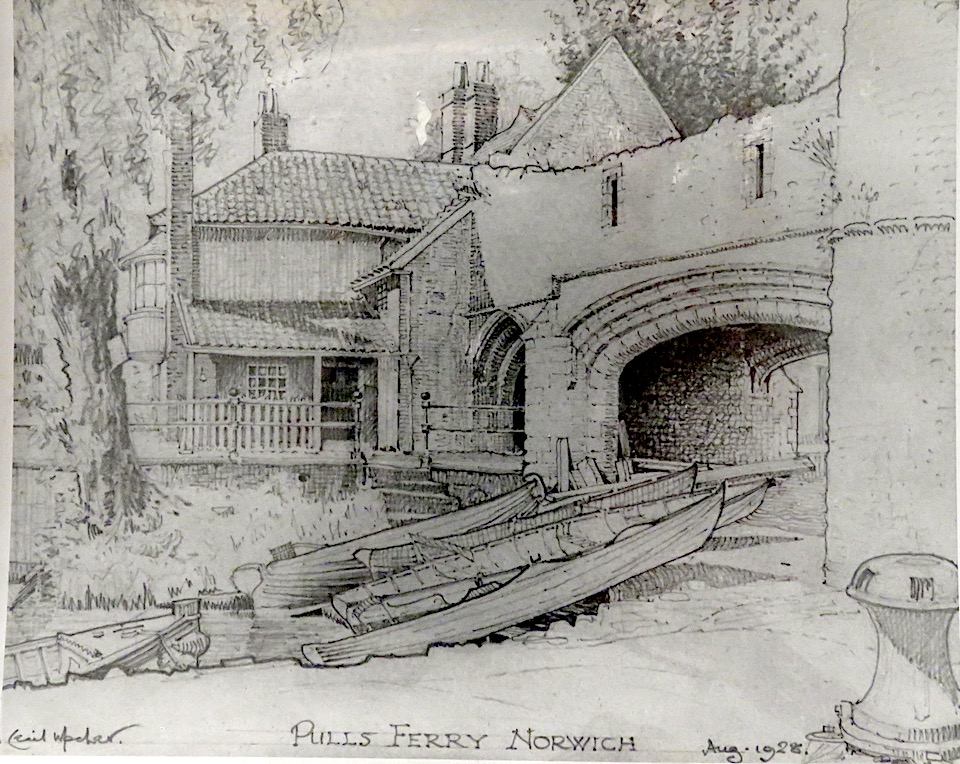
Sandling was superseded by John Pull who operated a pub here (Pull’s Ferry Inn or Ferry House) from 1796 until his bankruptcy in 1841 [12]. Pull’s Ferry operated until 1943 although it was already in ruin when Cecil Upcher drew the watergate in 1928.

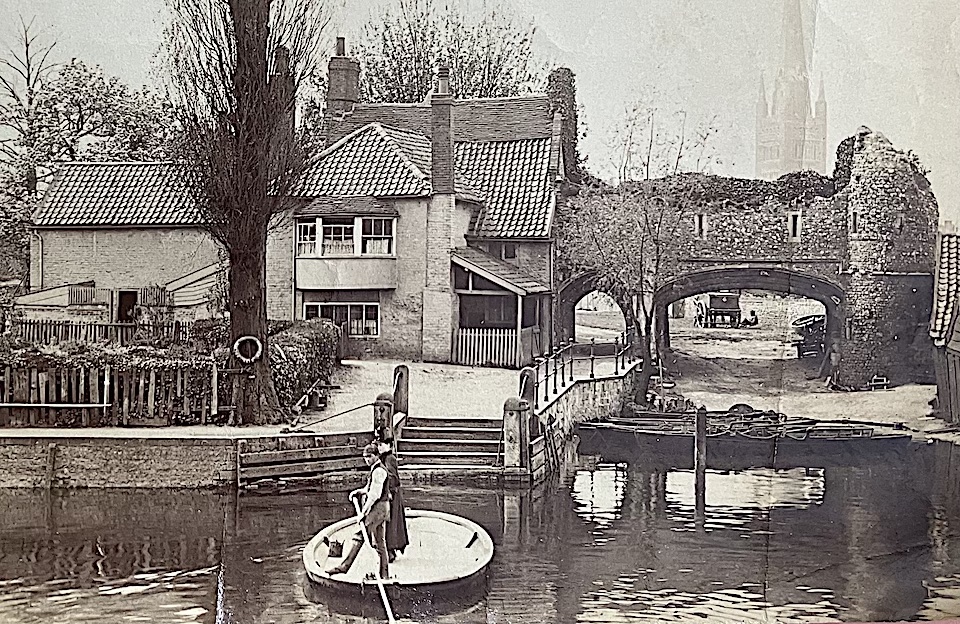
I had no idea of what the ferryboat itself looked like until April 2024 when I was given a photograph of Pull’s Ferry from what, from the clothing, appears to be the late Victorian era. The young ferryman transports a woman in a round squat boat propelled gondolier-fashion by a single oar.

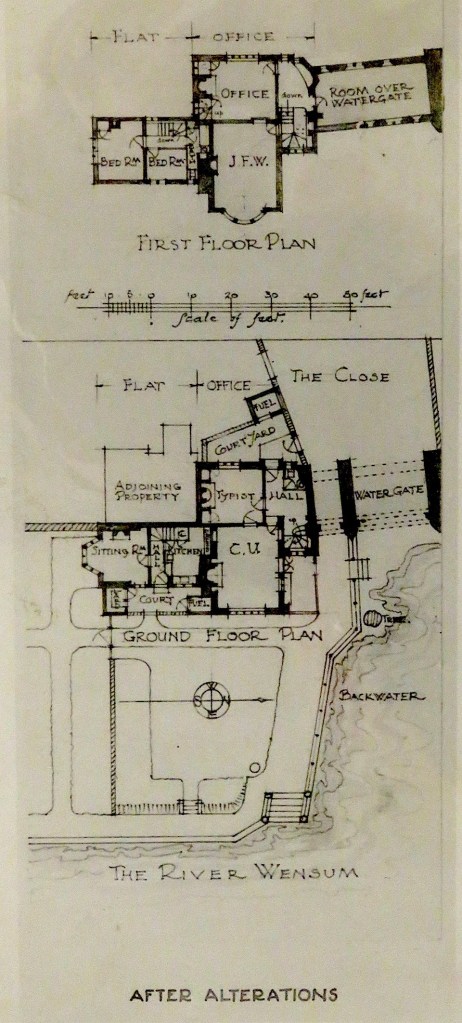
The Norfolk Record Office holds a small collection of photographs, possibly taken by Upcher himself. Wisely, they are sealed in plastic covers (I mention this to excuse the reflections on some of the following photographs). Upcher restored the house and watergate 1948-9.
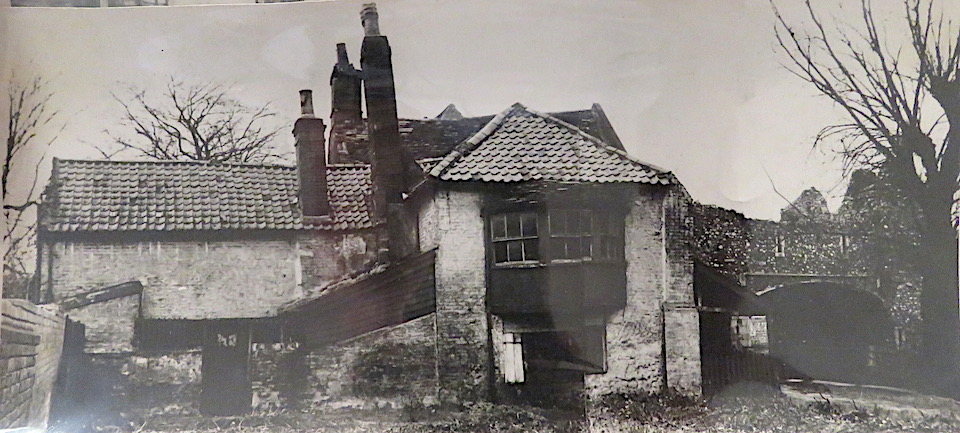
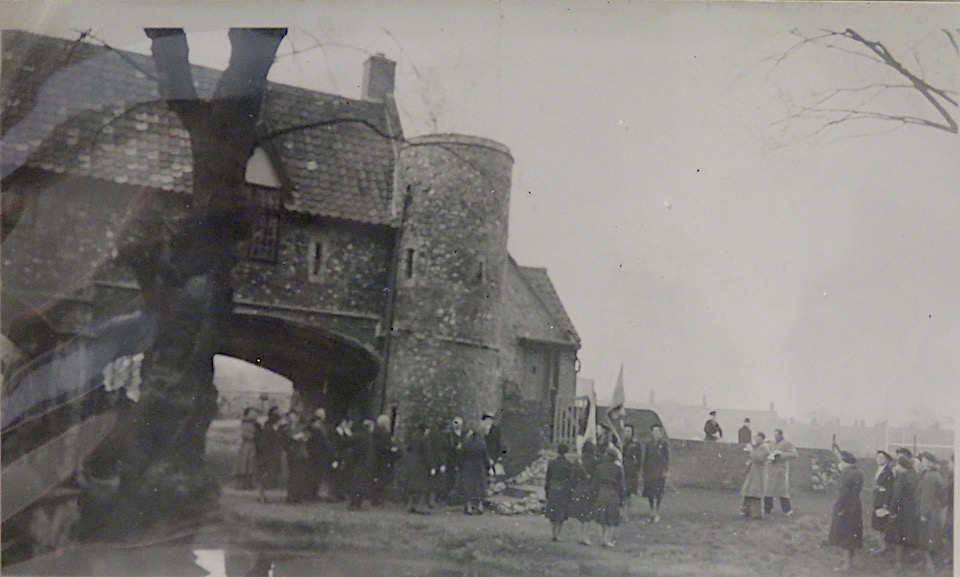




The restored Ferry House became offices for Upcher’s architectural practice but plans show that much of the space was dedicated to a two-storey flat – the only evidence of business being the small typist’s room on the ground floor and the office upstairs. The largest upstairs room, labelled ‘J.F.W.’, was allocated to Upcher’s nephew, James Fletcher-Watson. The largest room on the ground floor was C.U’s.
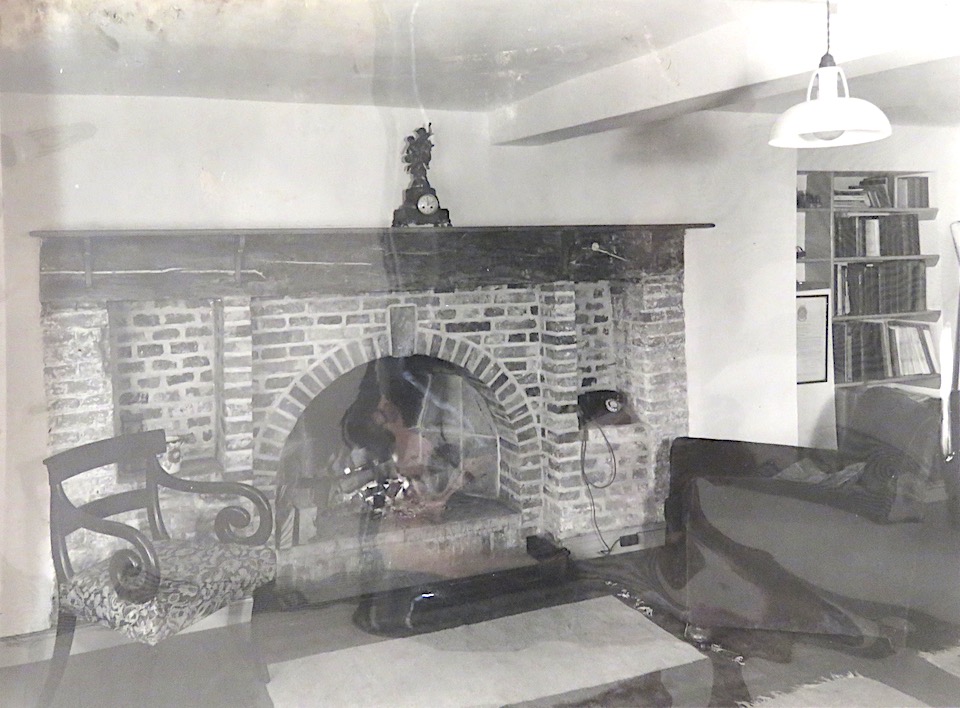
The photograph below, labelled ‘C Upcher’s room and armchair’, underlines how much space was dedicated to living accommodation.
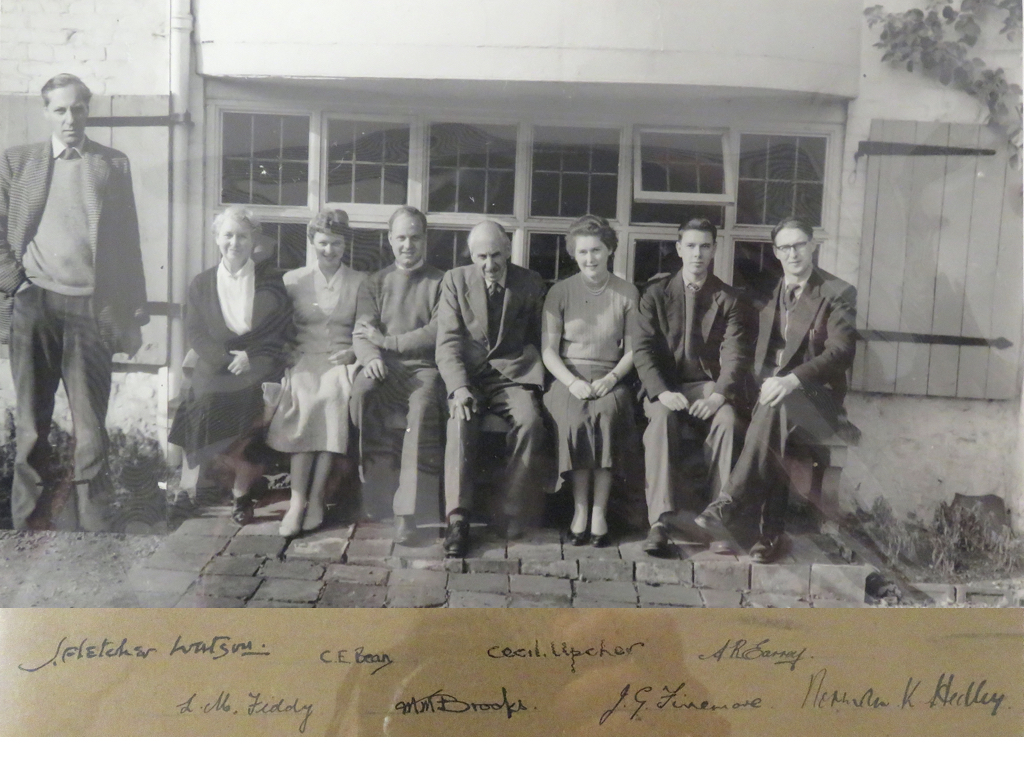


Standing on the left of the photograph is James Fletcher-Watson (1913-2004), with whom Upcher shared the practice. Trained as an architect under Edwin Lutyens, Fletcher-Watson is better known as one of the finest watercolourists of his generation.
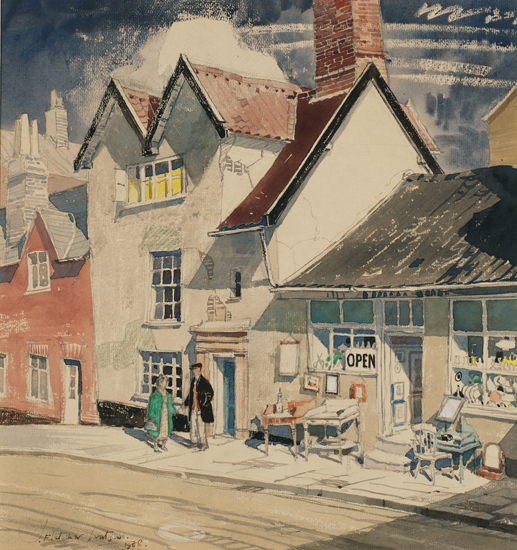

Cecil Upcher died age 88 and is buried in All Saints Upper Sheringham.

©2021 Reggie Unthank
Sources
- https://www.hiddenea.com/Survey%20A%20to%20B.htm
- https://www.genuki.org.uk/big/eng/NFK/Barnham_Broom/White1883
- https://your-family-history.com/surname/u/upcher/?year=1881#map
- Cecil Upcher letters Aug 1915 – Oct 1916. Royal Norfolk Regimental Museum.
- https://norfolkinworldwar1.wordpress.com/2015/09/
- Peter Bardwell’s Flickr page on Cecil Upcher: https://www.flickr.com/photos/132932913@N02/albums/72157682762647195
- Richard and Sarah Cocke (2013). Public Sculpture of Norfolk and Suffolk. Pub: Liverpool University Press.
- http://www.georgeplunkett.co.uk/Norwich/pri.htm#Prins
- Nikolaus Pevsner and Bill Wilson (2002). The Buildings of England. Norfolk I.Pub: Yale University Press.
- https://colonelunthanksnorwich.com/2021/05/15/af-scott-architectconservative-or-pioneer/
- Frank Meeres (2011). The Story of Norwich. Pub: Phillimore and Co Ltd, Andover.
- https://norfolkpubs.co.uk/norwich/pnorwich/ncppfi.htm
Thanks
I am grateful to Kate Thaxton, Curator, Royal Norfolk Regimental Museum for background on Upcher; to John Snape and Barbara Worland for Barnham Broom history; and to Gordon Blacklock at the Norfolk Record Office for guiding me through the Upcher archive.






















![Carrow Priory Prioress' parlour [3416] 1940-05-16.jpg](https://colonelunthanksnorwich.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/carrow-priory-prioress-parlour-3416-1940-05-16.jpg)
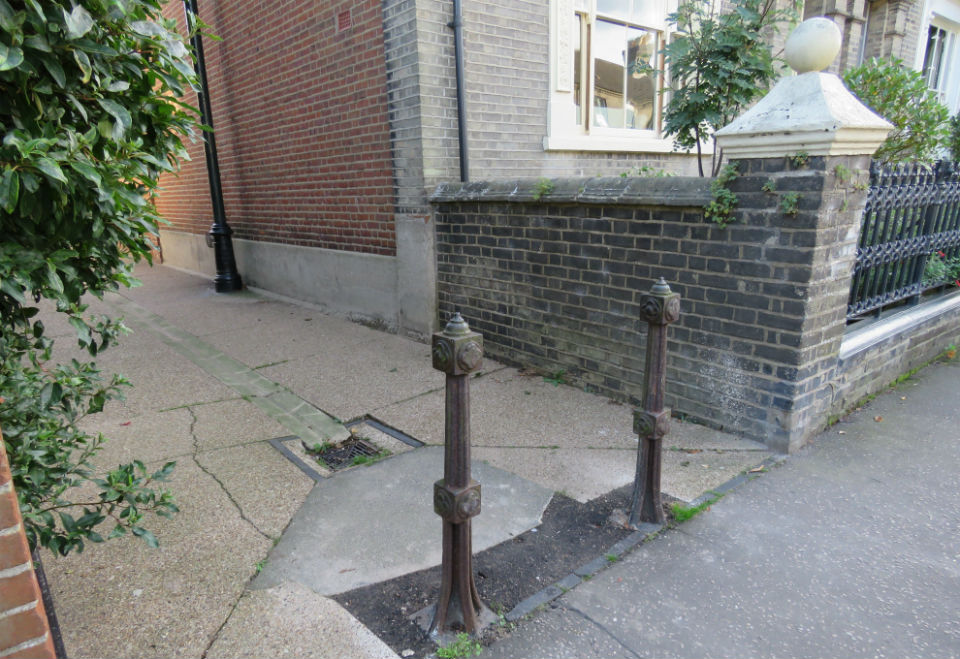









 The bollards in question guard the alleyway between Clarendon Road and Neville Street in the Heigham Grove Conservation Area. See the cast-iron railings on the adjacent house? The council’s own
The bollards in question guard the alleyway between Clarendon Road and Neville Street in the Heigham Grove Conservation Area. See the cast-iron railings on the adjacent house? The council’s own
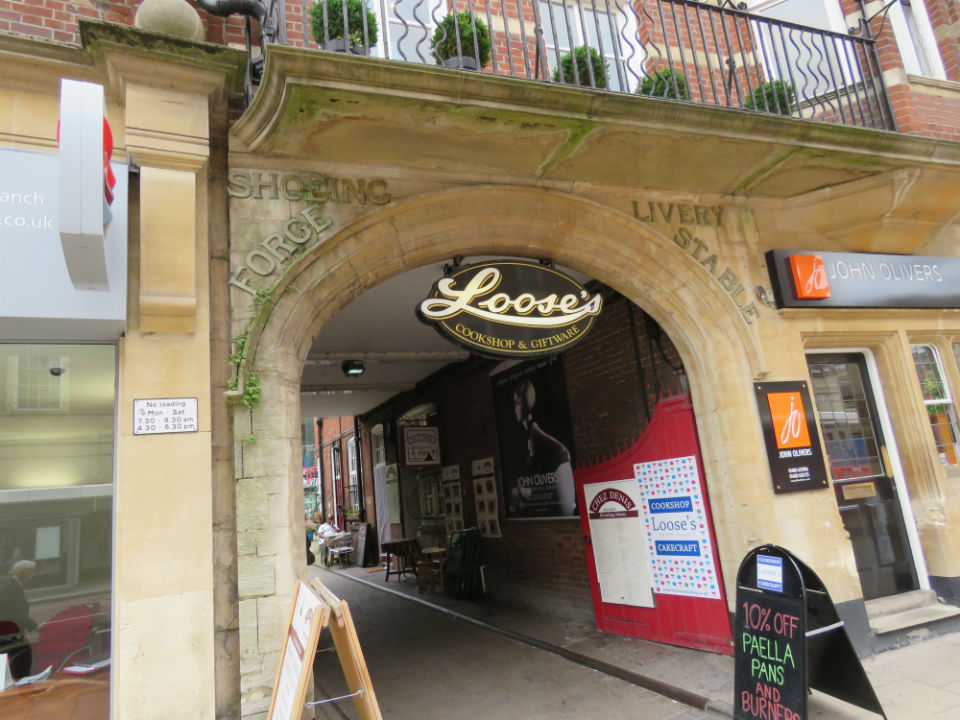


 The yard now accommodates Loose’s Cookshop and Chez Denis cafe and brasserie. Until 1998 the owner of Chez Denis had a previous business here, Cafe des Amis, the name of which can just be made out above the central arch in the photograph below.
The yard now accommodates Loose’s Cookshop and Chez Denis cafe and brasserie. Until 1998 the owner of Chez Denis had a previous business here, Cafe des Amis, the name of which can just be made out above the central arch in the photograph below.![Red Lion St Orford Yard former stables [7536] 1998-03-10.jpg](https://colonelunthanksnorwich.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/red-lion-st-orford-yard-former-stables-7536-1998-03-10.jpg)














![Duke St 4 Electricity works floodlit [1633] 1937-05-13.jpg](https://colonelunthanksnorwich.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/duke-st-4-electricity-works-floodlit-1633-1937-05-131.jpg)











![St Benedict's south side from church alley [0140] 1934-06-28](https://colonelunthanksnorwich.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/st-benedicts-south-side-from-church-alley-0140-1934-06-28.jpg?w=1024)
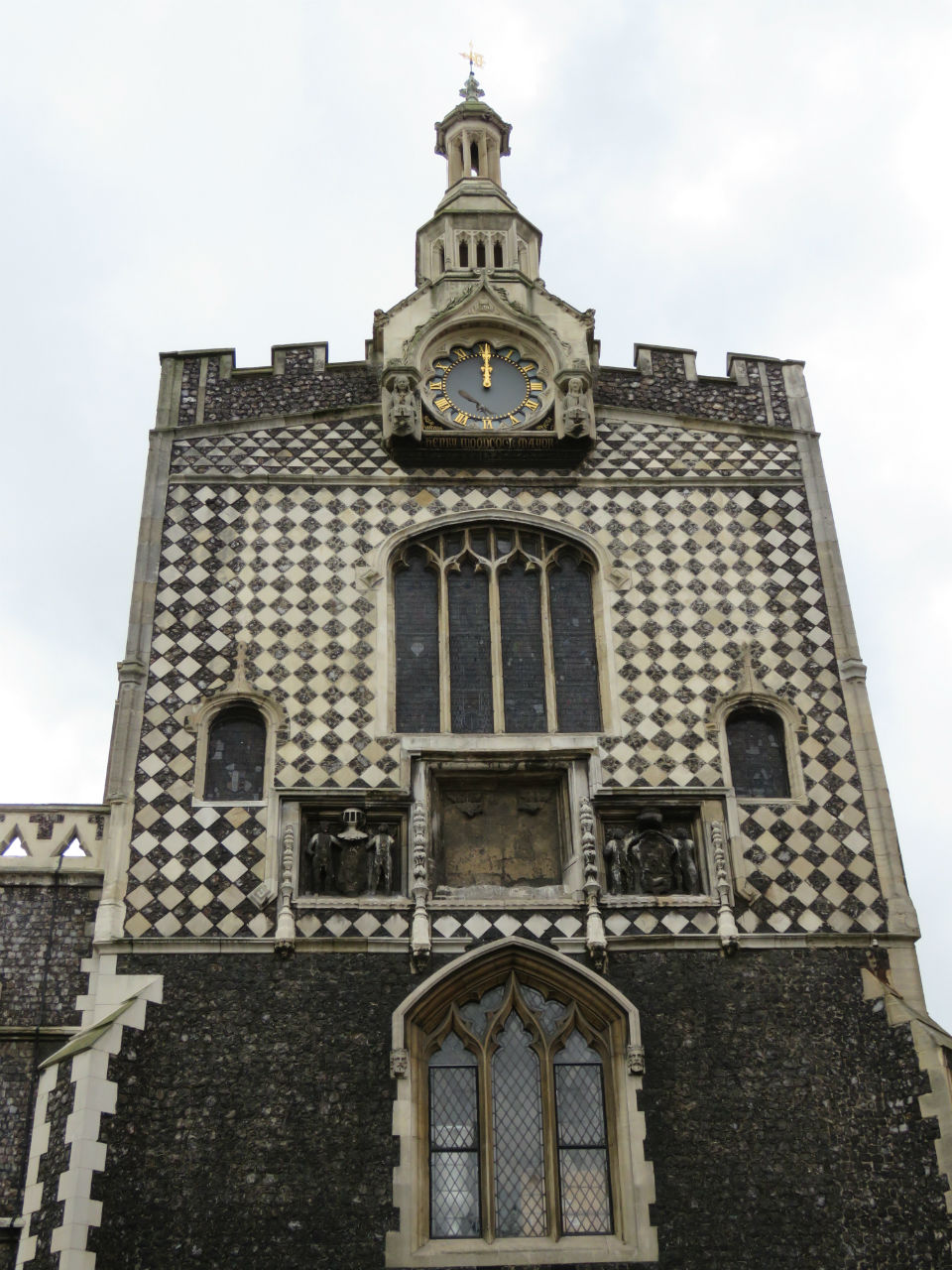
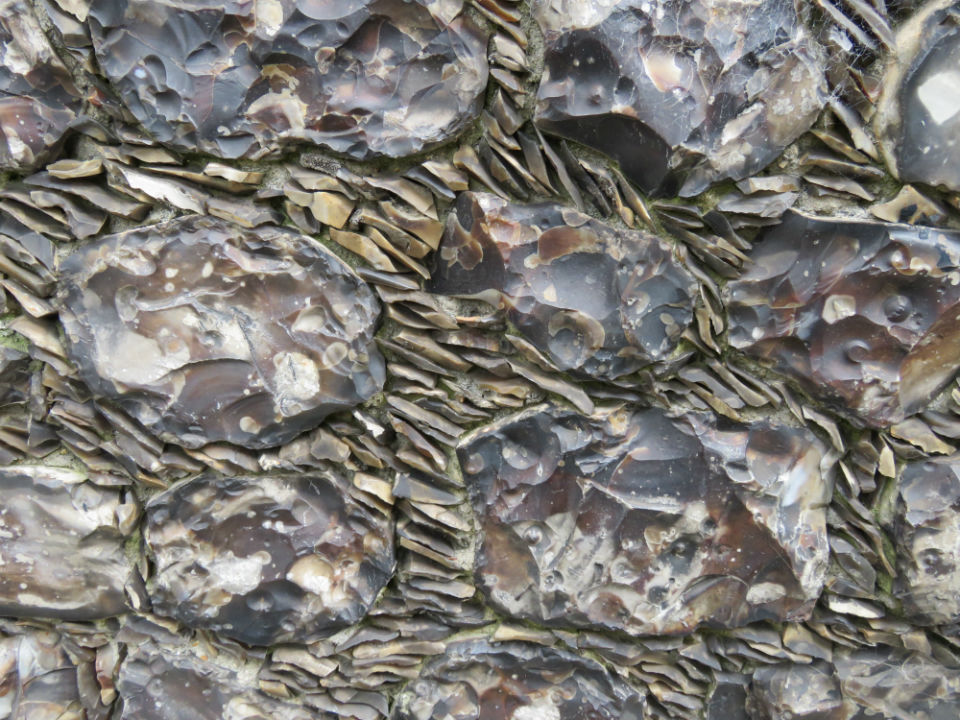
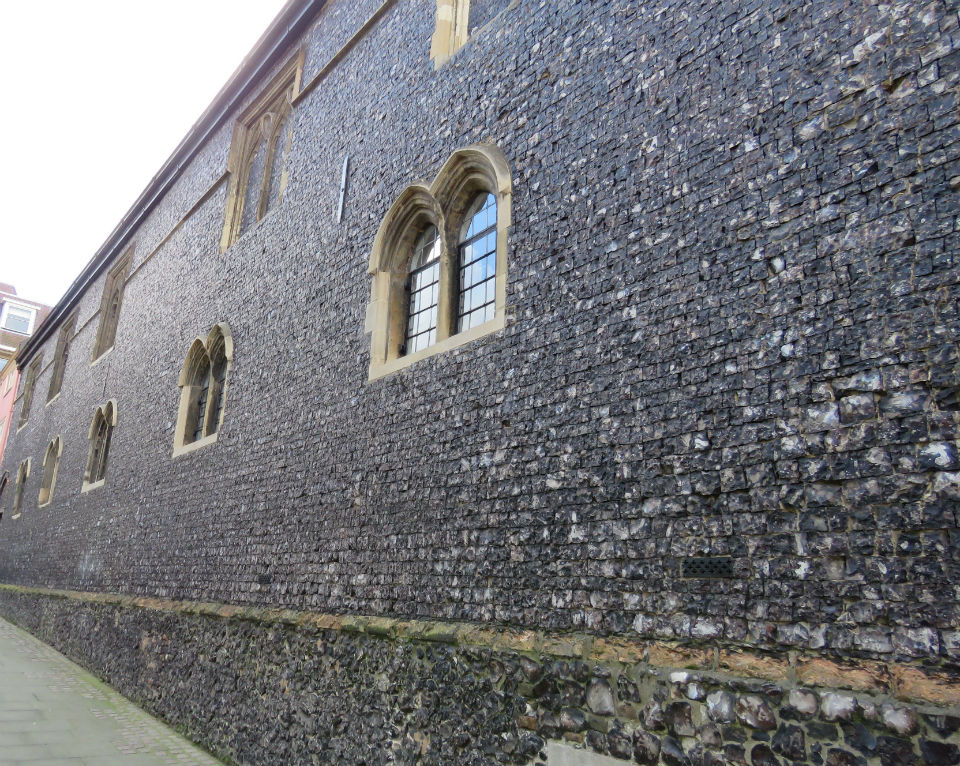
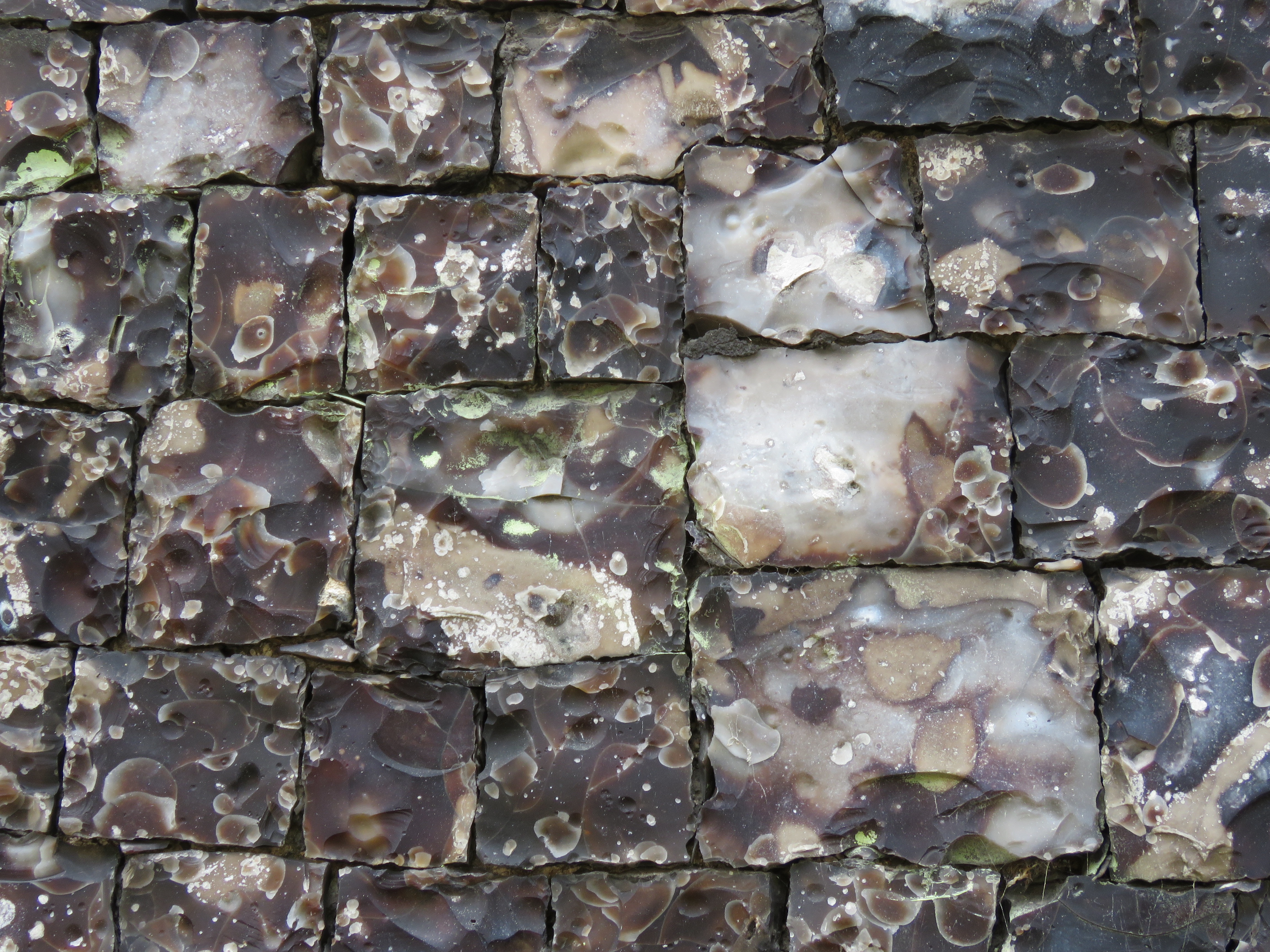



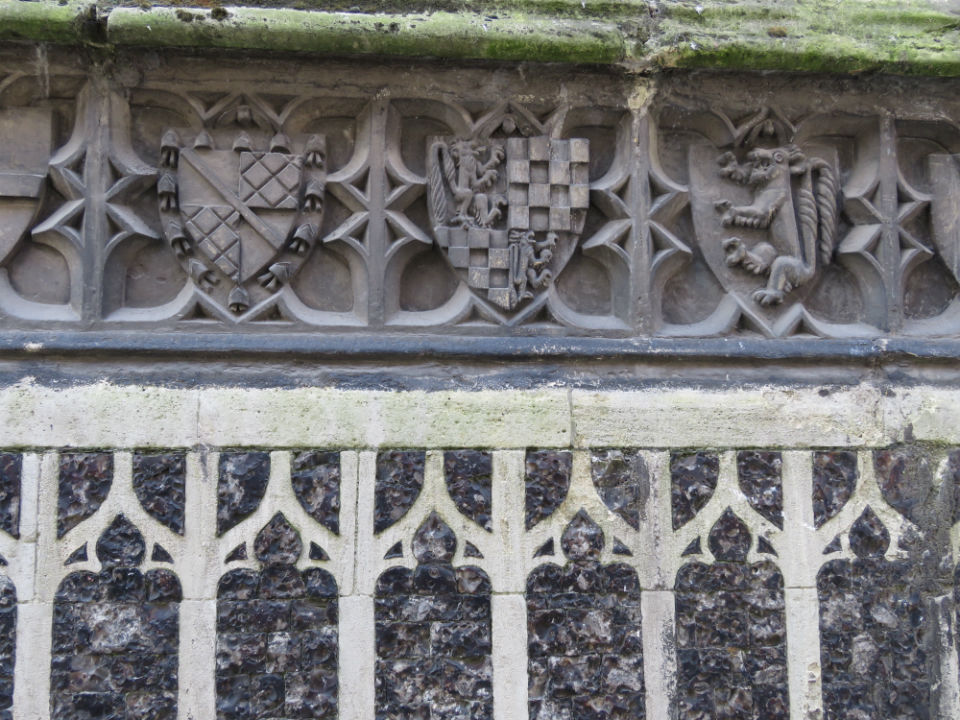
 Flushwork was a speciality of Norfolk and Suffolk and was at its most inventive during the Perpendicular Period (1330-1530) [7, 10]. St Michael (often contracted to St Miles) Coslany is a famously exuberant example. The artist John Sell Cotman claimed that the flushwork on the south side was “one of the finest examples of flint work in the kingdom” [11]. Parts of the church were rebuilt in the C19th. Here on the east end, restored in the 1880s, the flushwork mimics the tracery in the Perpendicular-style window next to it. This fits the general rule that representational designs were made in stone with flint in-fills while non-representational examples were in flint on a stone background [10].
Flushwork was a speciality of Norfolk and Suffolk and was at its most inventive during the Perpendicular Period (1330-1530) [7, 10]. St Michael (often contracted to St Miles) Coslany is a famously exuberant example. The artist John Sell Cotman claimed that the flushwork on the south side was “one of the finest examples of flint work in the kingdom” [11]. Parts of the church were rebuilt in the C19th. Here on the east end, restored in the 1880s, the flushwork mimics the tracery in the Perpendicular-style window next to it. This fits the general rule that representational designs were made in stone with flint in-fills while non-representational examples were in flint on a stone background [10].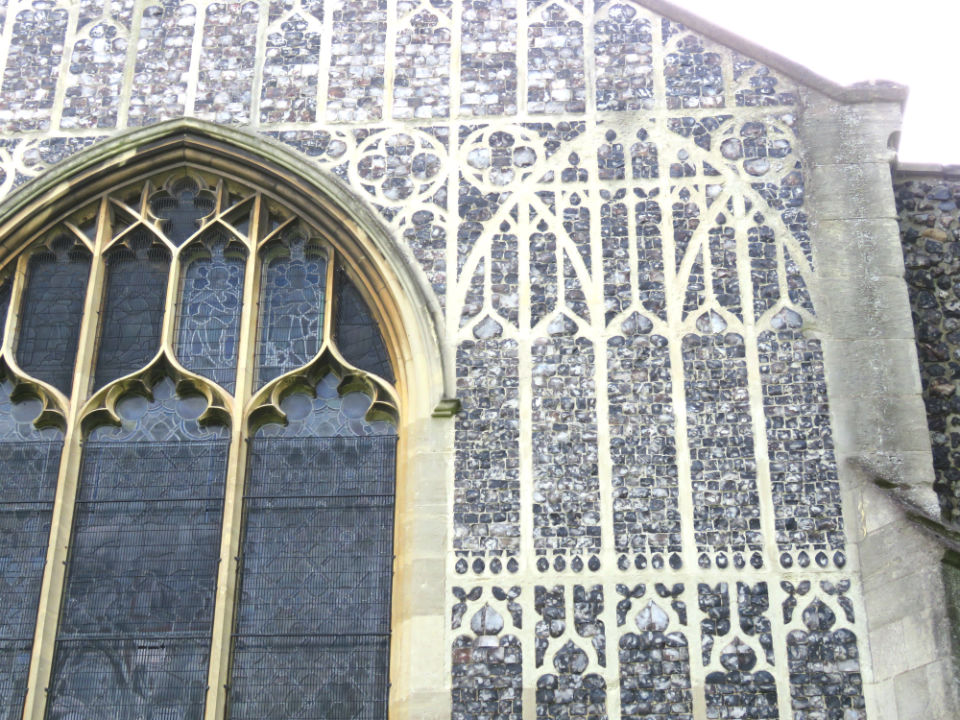











![St Giles' St 34 former Mortimer's Hotel [5278] 1969-08-16.jpg](https://colonelunthanksnorwich.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/st-giles-st-34-former-mortimers-hotel-5278-1969-08-16.jpg)
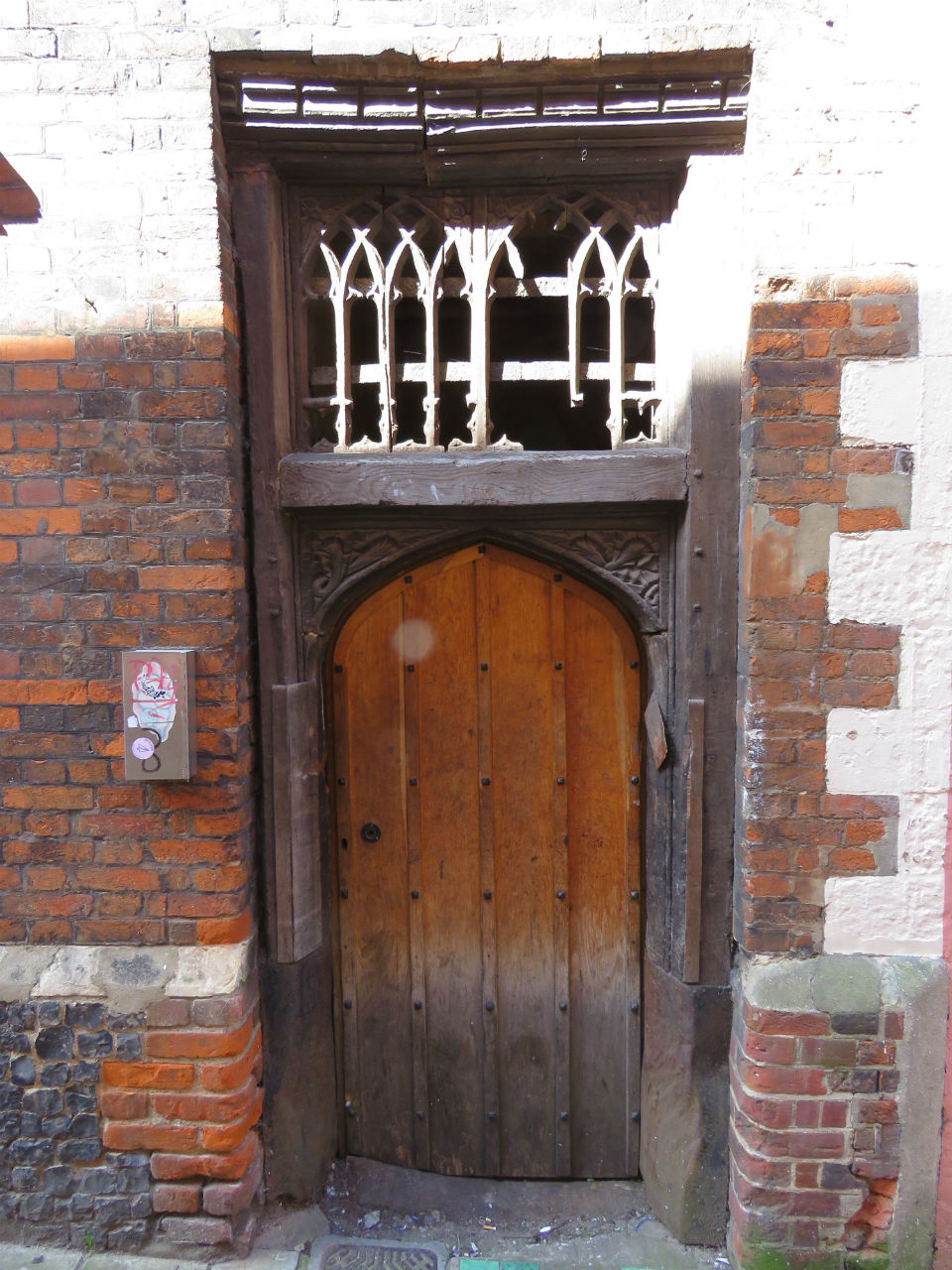
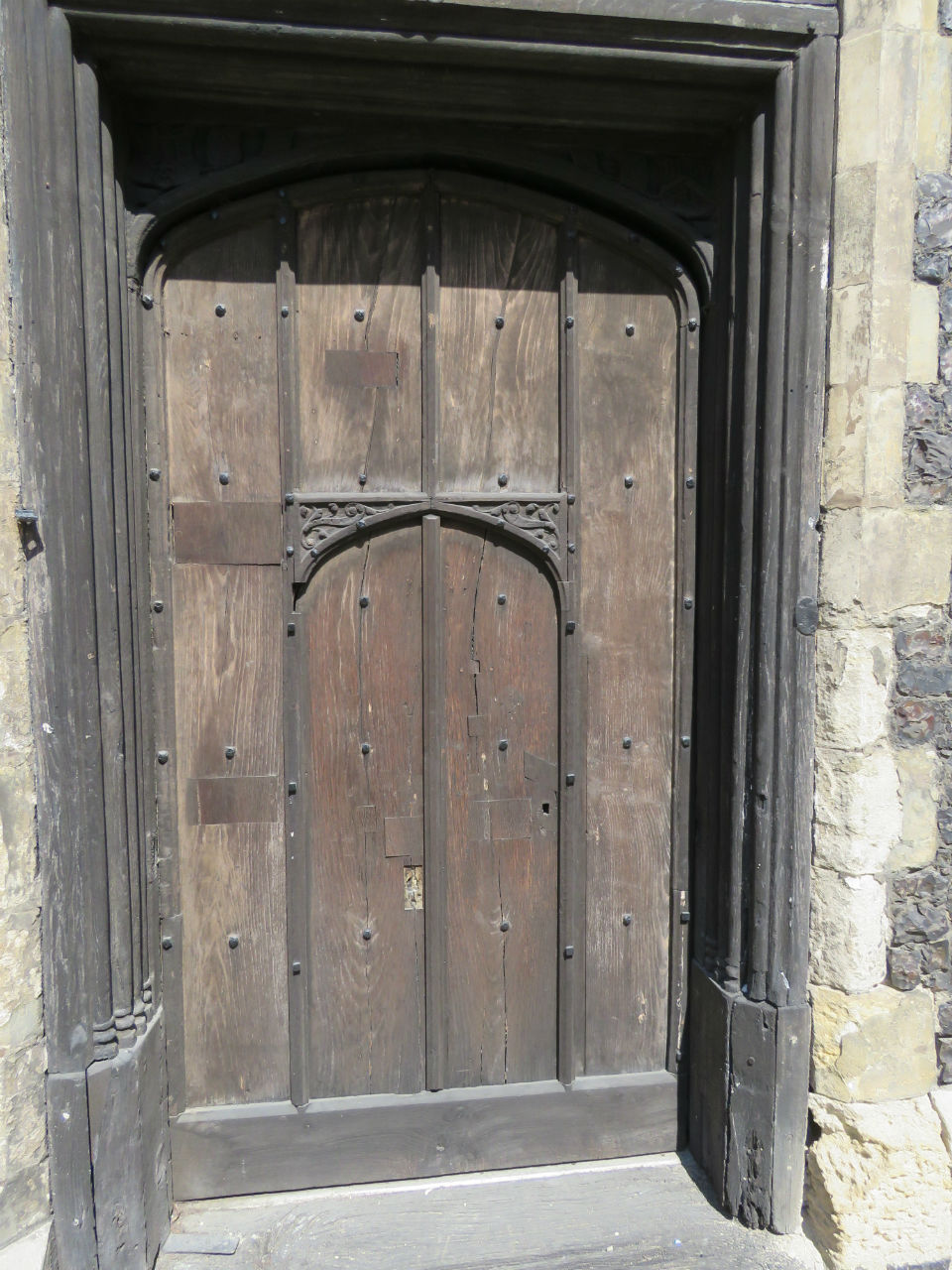






















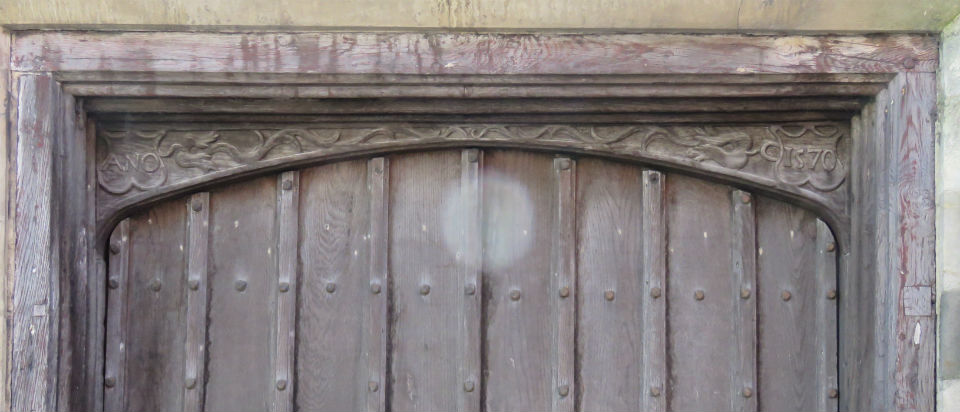
![Magdalen St Bayfield's Yard Tudor archway [0515] 1935-05-05.jpg](https://colonelunthanksnorwich.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/magdalen-st-bayfields-yard-tudor-archway-0515-1935-05-05.jpg)
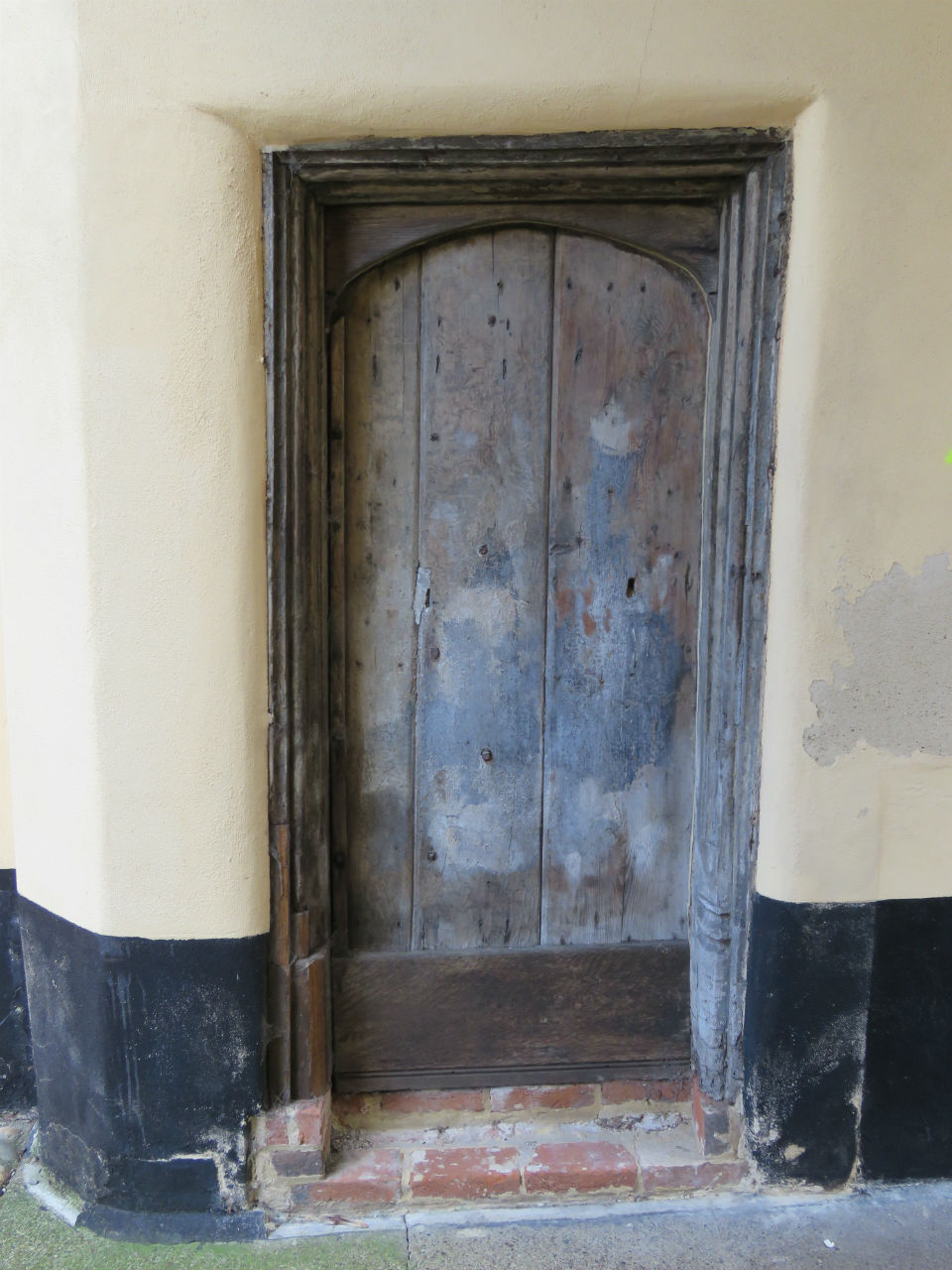
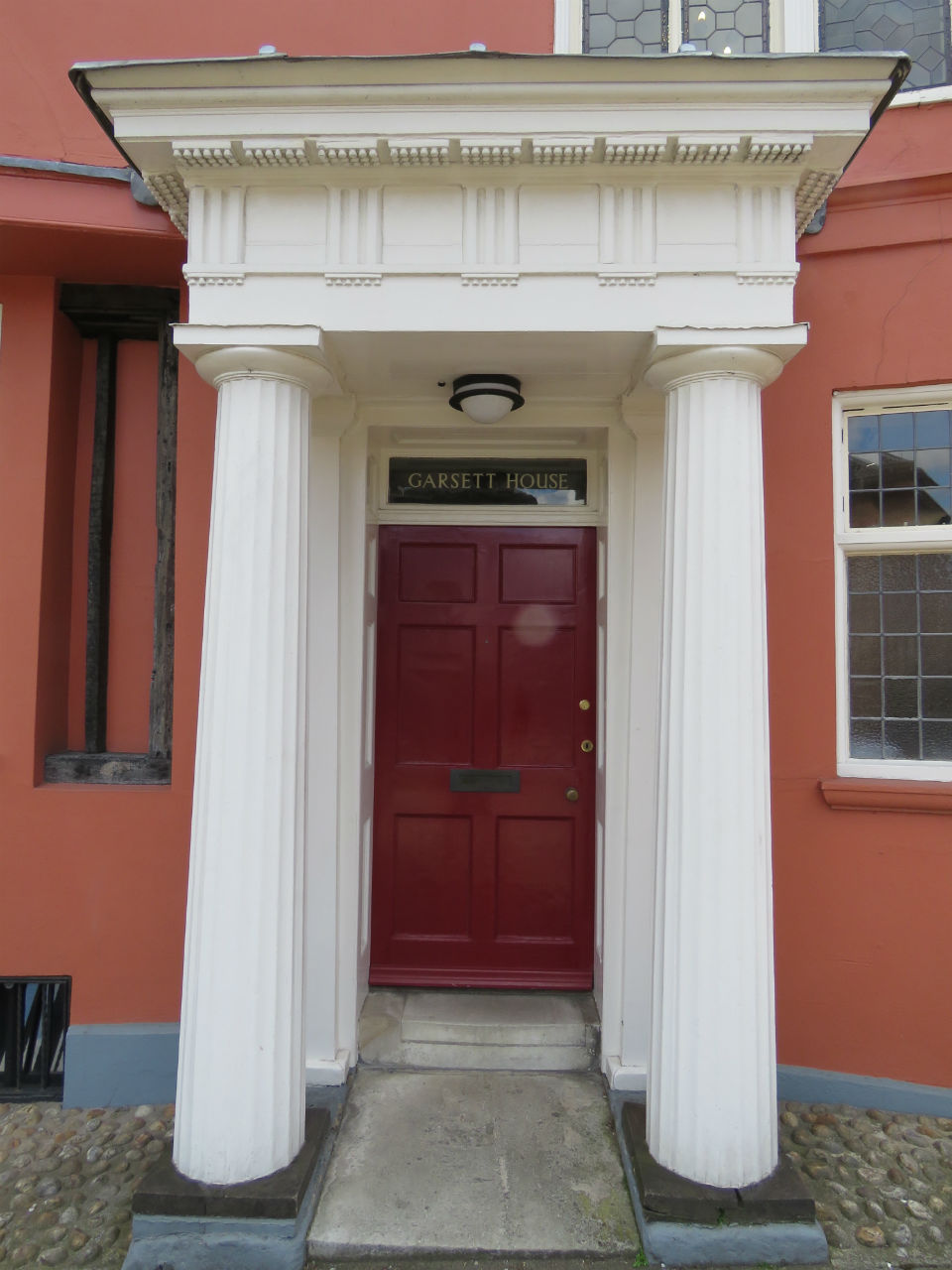
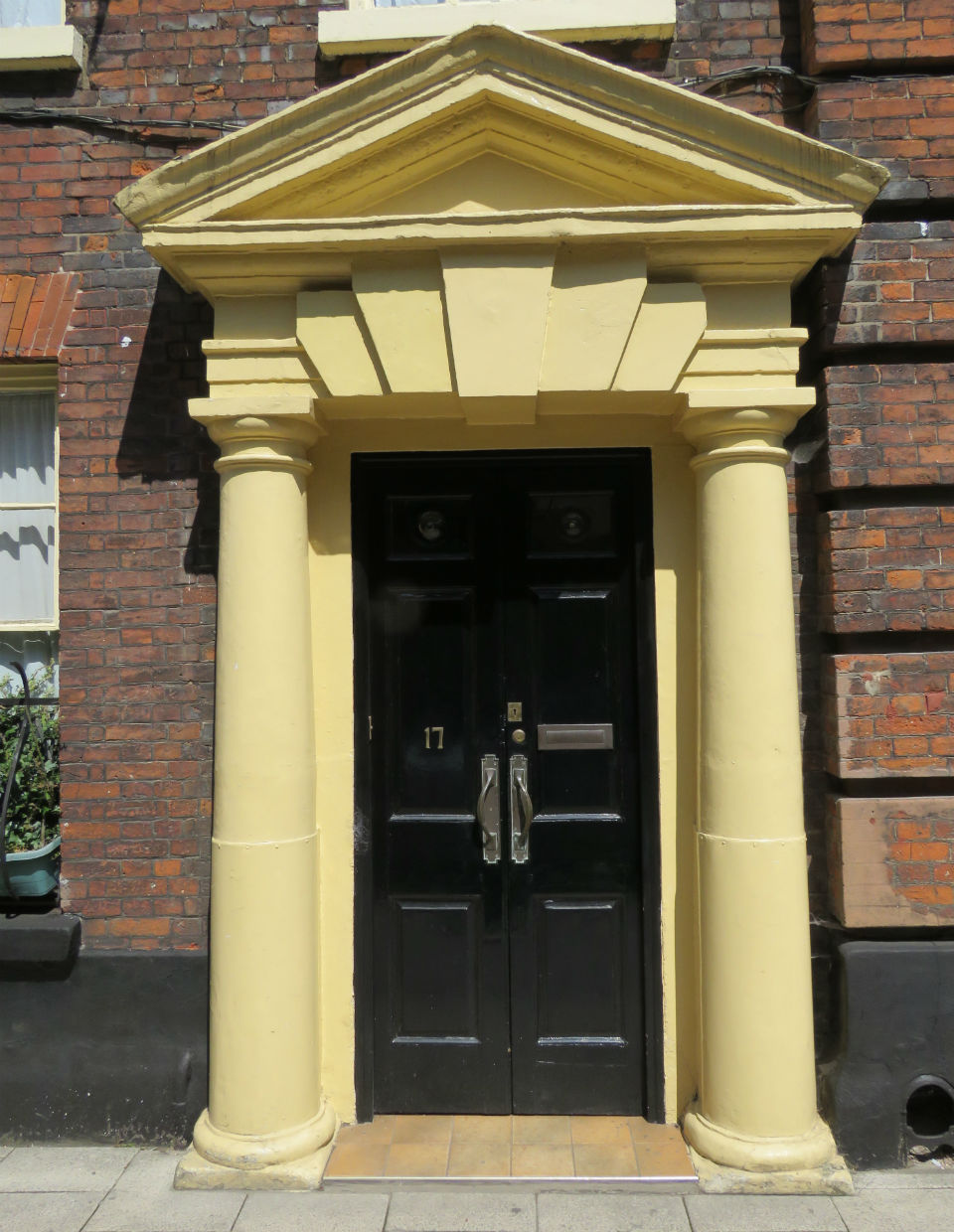
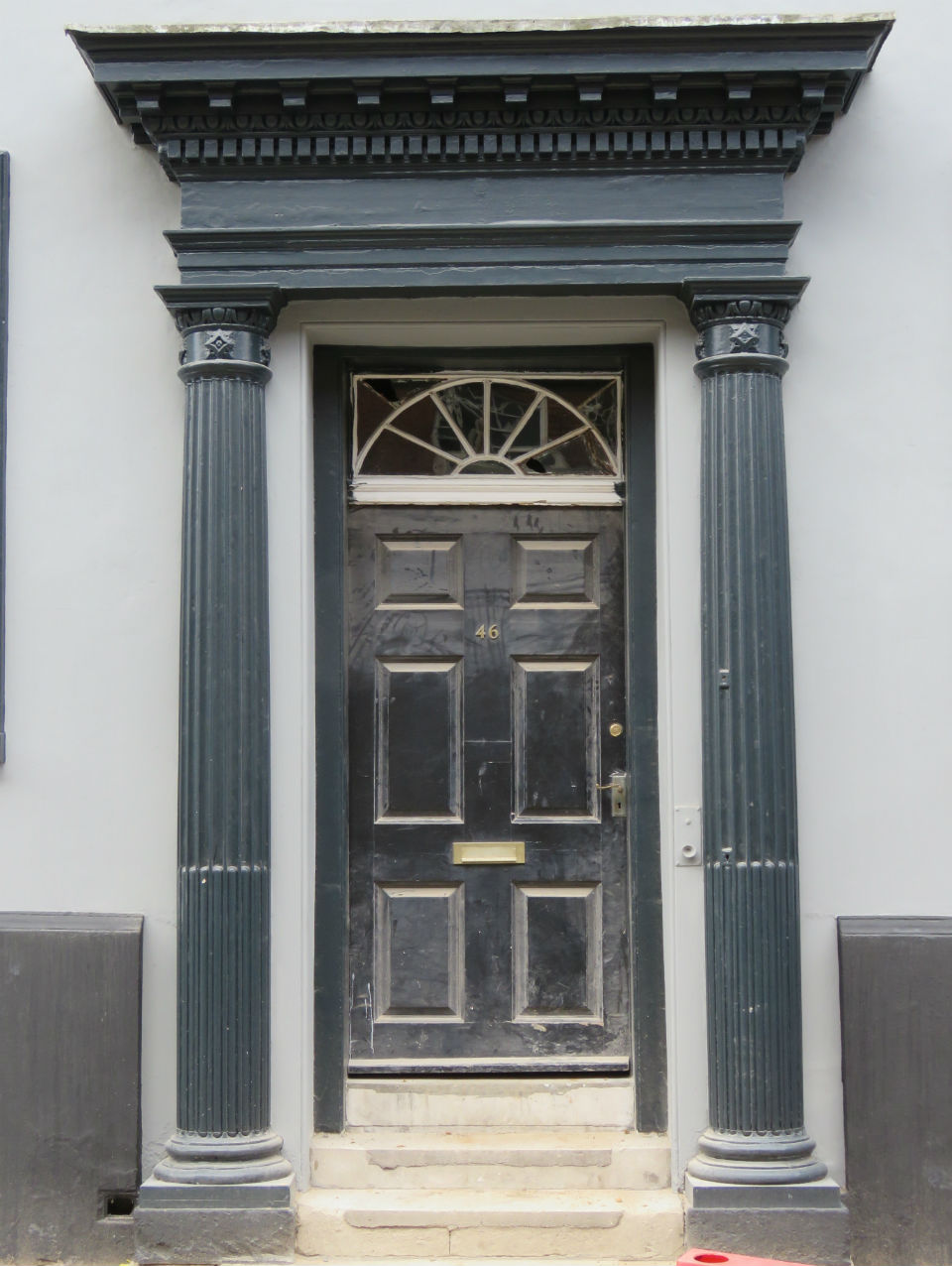
















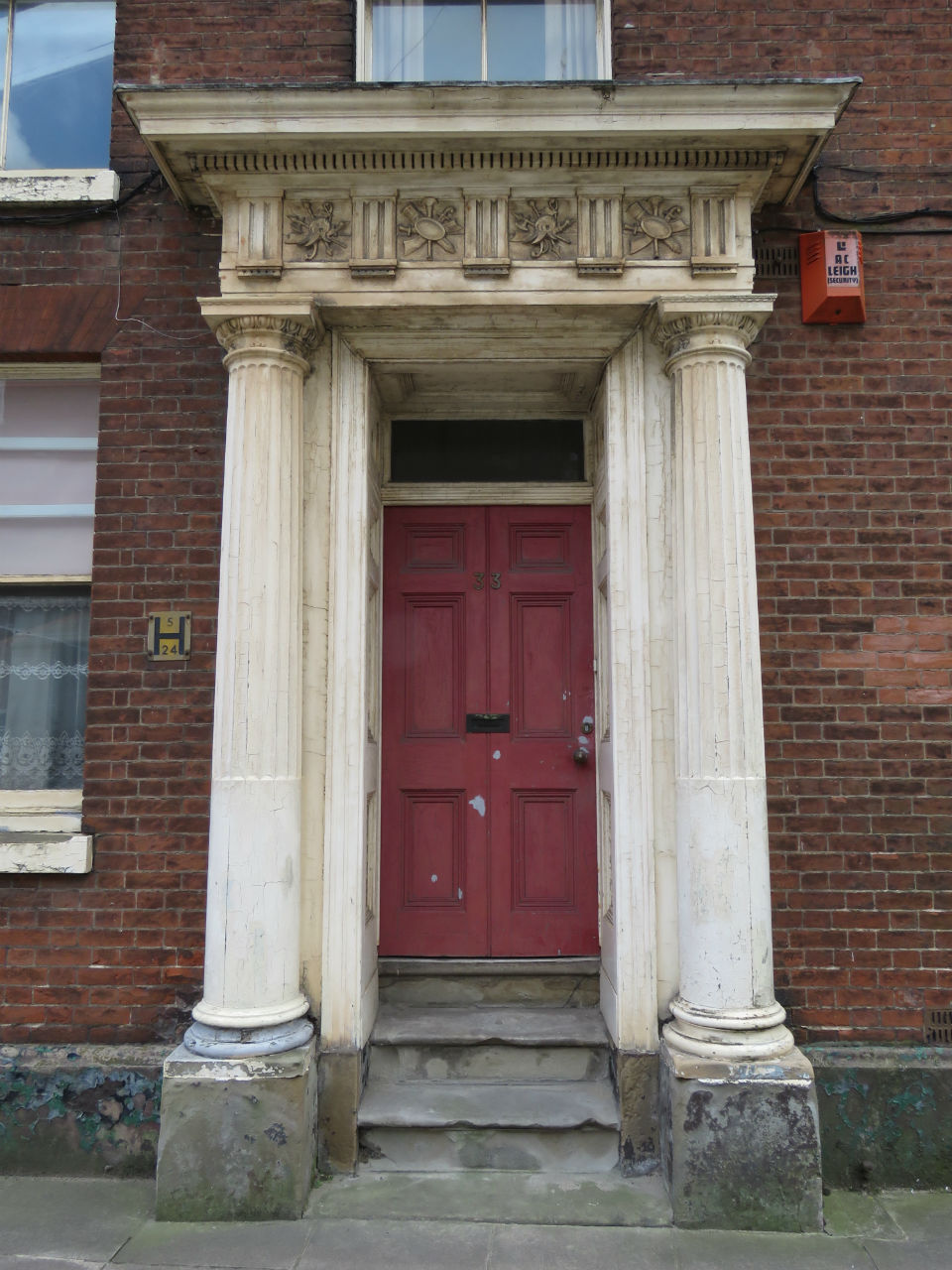
![Surrey St 25 to 27 Georgian portico [2187] 1938-03-21.jpg](https://colonelunthanksnorwich.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/surrey-st-25-to-27-georgian-portico-2187-1938-03-211.jpg)

![Surrey St 25 to 35 [0588] 1935-05-19.jpg](https://colonelunthanksnorwich.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/surrey-st-25-to-35-0588-1935-05-192.jpg)

